A Step-by-Step Guide to Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
This article discusses what an MVP is, why it is integral to a business, and how to build it within a short timeframe.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
As an entrepreneur, you should take the risk to validate your idea. First, you must decide whether your concept is feasible or not; is it really going to help customers? Your solution lies in an MVP. It will not only help you in validating your idea but also allow you to understand your customers' needs.
In this article, we will walk you through what an MVP is, why it is integral to a business, and how to build it within a short time frame.
What is an MVP?
MVP refers to the minimum viable product. In mobile app development, MVP is a basic version of an application. MVP is a process where a new product is developed with core functionalities, to test how the target audience would respond. Then, the actual product, with a full set of features, is developed after feedback is received from the early adopters.
MVP helps in testing, designing, and delivering the final product. MVP development plays an important role in web development and designing. Several businesses have pitfalls while trying to launch a minimum viable product for a mobile app or a web. That is why it is important to understand the build process of an MVP.
Purpose of an MVP
The purpose of an MVP is to launch a product quickly, based on your idea, with a small budget. This approach allows you to collect user's feedback for the primary product and include it in future iterations. With the help of an MVP, one can find the right audience, pull the ideas based on experience, and save time.
Building an MVP implies finding the right balance between what your business is offering to users, and what users actually need. The purpose of the MVP is to test the hypothesis by minimizing errors. An MVP helps in collecting maximum quality feedback, by targeting specific groups, or types of users.
Benefits of an MVP for your Business
Focus on building the core
An MVP app focuses on one idea, and it does not include any other function. The approach of the MVP belongs to the ideology of a lean startup, which is built with a minimal budget in a given time. Having some of the main features can reduce the cost of the mobile app development. The MVP allows the app to be tested, with minimal risk.
Early testing opportunity
It is good to find out from the beginning if your idea will work without investing your whole budget.
User intelligence and gathering feedback
The MVP offers the possibility to find out your potential users' opinion, and how they want to see your final product.
Allows market validation
An MVP helps you understand whether your app is right for your target market. It should present your brand well to the users, and show them how your project is unique compared to others in its category.
Takes less time to develop your app
Less development time means lower app development costs. The faster your mobile app is launched to users, the faster you will receive feedback. This means you can work on the improvement of your app, and release the updated version quickly.
Budget-friendly
This is yet another important advantage, as it avoids spending all of your resources right away, on things that may not work. Research shows that in 2017, the mobile app market grew considerably. Very few apps are actually downloaded from the many available, because of issues in their user interface and poor performance. Creating an MVP is an easy way to enhance the mobile development strategy.
The Need to Build an MVP
While starting up a business or launching a new product, have you ever invested time in the initial idea approval? If so, then an MVP is the right solution to get to work on your idea from the beginning and test it quickly for launch. Below are the reasons why you need MVP development:
- Creating an initial model - this gives a start point for discussions and offers clear visual points of reference.
- Conducting initial idea approval - this includes sharing the model with a few prospects, and testing it with genuine users, to better understand issues you may face with your innovation.
- Preparing to begin your journey - you have invested months improving your software idea, but to actually start building your product can feel like a big deal. An MVP prepares you to take that hike.
While building a mobile app, you must understand that the whole idea of MVP is divided into two main parts. The first part refers to business and marketing; because of the MVP, you are now able to launch a survey to find those best marketing approaches and the advertising platforms that could be used for the advancement of your product.
The second part refers to the technical aspect. Through an MVP, you will be able to execute important programming and designing features, which, in turn, will help you make your app unique.
Steps to Building an MVP
The MVP is all about testing your idea and figuring out what exactly will work to properly target your customers, and ensuring that the MVP meets their needs. If everything has been done correctly, then it will be much easier to finalize the product and market it later.
Below are the necessary steps to build an MVP:
Step 1: Market Research
At times, it happens that ideas do not fit into the market needs. Before you initiate an idea, ensure that it fulfills the target users' needs. Conduct surveys, because the more information you have, the higher your chances are of success. Also, do not forget to keep an eye on what your competitors are offering, and how you can make your idea unique.
Step 2: Express Your Idea
What value does your product offer to its users? How can it benefit them? Why would they buy your product? These are important questions to keep in mind to help better express your idea.
You should also be clear about the essential estimations of your product. As MVP implies, introducing value to the people, first outline them and based on that develop your MVP.
Step 3: Consider the Design Process & User Flow
Design the app in a way that is convenient for users. You need to look at the app from the user's perspective, starting from opening the app to the final process, such as making a purchase or delivery. In addition, user flow is an important aspect as it ensures you do not miss anything while keeping the future product and its user satisfaction in mind.
To define your user flow, it is necessary to define the process stages, and for that, you need to explain the steps needed to reach the main objective. Your focus should be more on basic tasks rather than features such as finding and buying the product, and managing and receiving orders. These are the goals that your end users will have while using your product. When all these procedure stages are clearly laid out, it is time to define the features of each stage.
Step 4: List the Project Features
First of all, list all the features that you want to incorporate into your product before you start building the MVP; and, once the building process is completed, cross-check with the list. When you have a list of features for each stage, you then need to prioritize them. To prioritize the features, ask yourself questions such as, "What do my users want?" and "Am I offering them something beneficial?"
Next, categorize all the remaining features based on priority: high priority, medium priority, and low priority. When you have organized all the features, you can define their scope for the first version of the product, and move to building an MVP. If you want to see how your future product will look, you can even create an MVP's prototype.
Step 5: Build your MVP
Once you have decided upon the main features and have learned about the market needs, you can create your MVP. Keep in mind that a prototype is not lower quality than a final product, and still needs to fulfill your customer's needs. Therefore, it must be easy to use, engaging, and suitable for your users.
Step 6: Build, Measure, and Learn
Everything is part of a process: first, the scope of work is defined, and the product is moved to the development stage. After the completion of product development, the product needs to be tested. Quality Assurance engineers, who work to improve the quality of the product (even if the product is not released) conduct the first testing stage.
Review everything thoroughly after launching the MVP, i.e. collect your client's reaction to the release. With their feedback, you can determine if the product is acceptable in the market if is it competing with the other products in the market, and so on.
It is important to realize that users tell us where the product is lacking and what features are not needed. Once you collect the feedback from the users, start improving your product, then test, learn, and measure the quality, and then test again, and the process goes on until it is finalized.
Remember!
Always listen to your users
You are building products for the users' benefit
Never hesitate to ask your users what they want
Measuring Success after Building MVP
There are several approaches to give a real picture of the future success of your product, here are the most common, effective, and proven ways to measure the success of an MVP:
Word of mouth
Traffic is a useful metric to predict the success. Another way to track success is interviewing potential customers. You can start by listing the problems you assume a customer is facing or might face, and ask them what they think.
Engagement
It enables you to measure not only the current value of the product but also the future value. Engagement helps to improve the user experience based on feedback.
Sign-up
Sign-ups are a feasible way to gauge user interest, and they may convert to revenue, based on the results of measuring interest in your product.
Better client appraisals based on the feedback
The number of downloads and launch rates shows whether users' are interested in your app or not. The lighter your app is, the more downloads it will get.
Percentage of active users
Download and launch rates are not the only things used to measure the success of an MVP. You need to study users' behavior, and regularly check the ratings of active users.
Client acquisition cost (CAC)
You must know how much it costs to get a paying customer. This helps you stay updated on whether your marketing efforts are effective, or changes need to be made. CAC = Money spent on traction channel / Number of customers acquired through the channel.
Check the number of paying users
Know the average revenue per user (ARPU), and keep a check on products that bring revenue. ARPU= Total income for the day and age/Number of active users
Client Lifetime Value (CLV)
It demonstrates how much time a user spends on the app before uninstalling, or stopping to use it. CLV= (Profit from a user *App usage duration) - Acquisition cost
Churn
It shows the level or percentage of people who have uninstalled or stopped using your app. Churn = Number of churn per week or month / Number of users at the beginning of the week or month
Companies That Successfully Launched MVPs
Here are a few notable companies that launched MVPs successfully. This goes on to show what startups focus on when it comes to developing a key MVP feature set.
 When Facebook was launched, an MVP was done just to connect students of schools and colleges all together via messaging. The idea was just to connect friends through a social platform, and organize gatherings. Facebook, in its early days, was built on the basic model of an MVP containing the needed functionality to fulfill its goal. This application was launched to test among users, and it gathered lots of feedback. This resulted in making the application extremely popular over the internet, it currently has over 1.3 billion active users.
When Facebook was launched, an MVP was done just to connect students of schools and colleges all together via messaging. The idea was just to connect friends through a social platform, and organize gatherings. Facebook, in its early days, was built on the basic model of an MVP containing the needed functionality to fulfill its goal. This application was launched to test among users, and it gathered lots of feedback. This resulted in making the application extremely popular over the internet, it currently has over 1.3 billion active users.
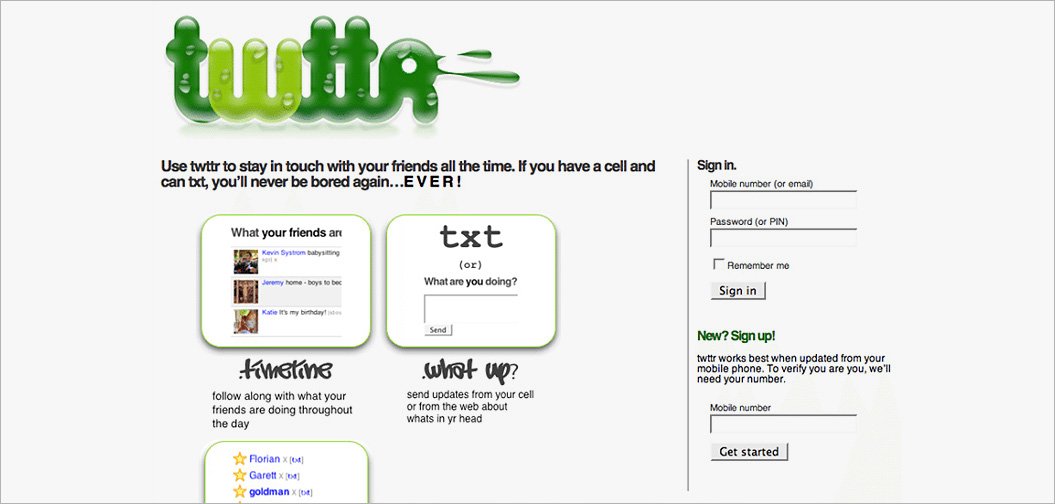 A widely popular social media platform, Twitter, involves a unique approach. After Apple released iTunes, a podcasting platform, Odeo, experienced tough times and they were forced to organize hackathons, trying to figure out what to do next. During one of their hackathons, they came up with an idea to create an SMS-based platform. It was initially known as “twttr”, and was a product for internal use only. However, employees were spending several dollars on SMS to post to the platform, in order to test it among users. Finally, Twitter was released to the public in 2006, a year later it was a hit. Twitter increased its userbase, and became the second most popular social networking site after Facebook.
A widely popular social media platform, Twitter, involves a unique approach. After Apple released iTunes, a podcasting platform, Odeo, experienced tough times and they were forced to organize hackathons, trying to figure out what to do next. During one of their hackathons, they came up with an idea to create an SMS-based platform. It was initially known as “twttr”, and was a product for internal use only. However, employees were spending several dollars on SMS to post to the platform, in order to test it among users. Finally, Twitter was released to the public in 2006, a year later it was a hit. Twitter increased its userbase, and became the second most popular social networking site after Facebook.
Amazon

Amazon was started to sell books online, by challenging the Barnes and Nobles of the world who were largely stuck in the bricks and mortar age. Originally designed in 1994 to focus on books at a low price, with an easy web design based on an MVP, that’s all they needed to develop and establish their organization in the retail market.
Groupon
 Using the old concept of vouchers and discounts, with an idea of sharing and socializing, Groupon has attained new heights. Initially, Groupon was launched using WordPress, where regular PDFs were emailed to users that were already subscribed. Testing with the help of an MVP proved successful. Afterward, Groupon built its voucher system and backend, further driving it to a great achievement.
Using the old concept of vouchers and discounts, with an idea of sharing and socializing, Groupon has attained new heights. Initially, Groupon was launched using WordPress, where regular PDFs were emailed to users that were already subscribed. Testing with the help of an MVP proved successful. Afterward, Groupon built its voucher system and backend, further driving it to a great achievement.
Dropbox
To Conclude
An MVP aims at solving users core problems with the app, by identifying the pain points and then focusing on offering viable solutions. The best way to build an MVP is to use a manual-based approach, with landing pages, and email lists. All you need is brainstorming, planning, designing & developing, testing, and advertising, for the product within a specified period. This results in maximizing your project’s value to potential customers.
Need any help in building an MVP for your project, or need a consultation? Reach out to us at . Also, please share your feedback or experience with us in the below comments section.
Published at DZone with permission of , DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments