Achieving Continuous Compliance: Ensure Success With Key Components and Security Automation
See the challenges of maintaining compliance to protect data and avoid legal issues. Learn security automation's role in achieving compliance with GDPR and HIPAA.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is an article from DZone's 2023 Enterprise Security Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
If you've ever explored regulatory compliance and cybersecurity, you'll understand the importance of continuous compliance in the digital age, where evolving technology and regulations require constant vigilance.
This article will cover the challenges of maintaining compliance to protect data and avoid legal issues, emphasizing security automation's role in achieving compliance with frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA. It will offer practical insights for businesses to successfully navigate this dynamic environment.
Understanding Compliance
In the context of IT and business, compliance involves adhering to a set of established guidelines or regulations that are often mandated by law. These regulations are designed to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data, especially when it concerns sensitive information like personal data or health records. Compliance ensures that organizations operate within legal and ethical boundaries, thus safeguarding not only their data but also their reputation and operational continuity.
Common Regulations and Standards
Several regulations and standards have been established globally to guide organizations in managing and protecting data. Notable among these are:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – This is a "regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy in the European Union and the European Economic Area. It also addresses the transfer of personal data outside these areas" (VMWare Information Security and Regulatory Compliance Glossary).
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – This U.S. legislation provides data privacy and security provisions for safeguarding medical information. It's crucial for organizations in the healthcare sector and those handling health-related data.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) – This standard mandates security measures for organizations that handle credit card transactions to reduce credit card fraud.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
The implications of not adhering to these compliance standards can be severe. They include:
- Financial penalties – Organizations can face hefty fines for non-compliance. For instance, GDPR violations can result in fines of up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million (whichever is greater).
- Reputation damage – Non-compliance can lead to a loss of trust among customers and partners, which can be devastating for a business' reputation and long-term sustainability.
- Operational disruptions – Regulatory bodies may impose restrictions on non-compliant organizations, potentially leading to interruptions in business operations.
- Legal consequences – In some cases, non-compliance can lead to legal action against the company or its officers, resulting in further financial and reputational damage.
What Is Continuous Compliance?
Continuous compliance is an ongoing process that integrates compliance management processes into daily operations, which is crucial in today's fast-evolving digital landscape. It contrasts with traditional compliance, which relies on periodic checks and audits. Key features include proactive monitoring, automated compliance checks, and a frequent, responsive approach.
Continuous compliance ensures organizations constantly align with current standards, allowing for immediate responses to regulatory changes or IT environment shifts, which thereby enhances adaptability and effectiveness.
Benefits of Transitioning to a Continuous Compliance Model
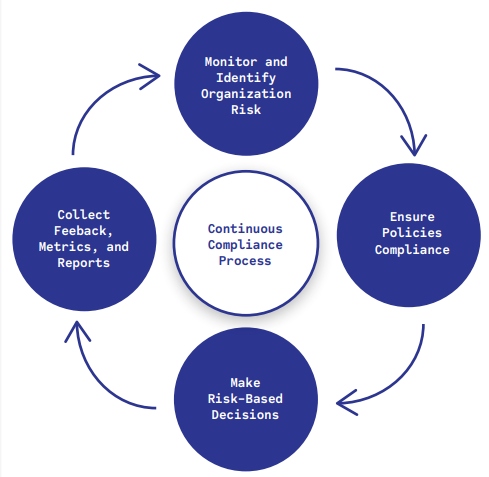
Figure 1: Continuous compliance process
Transitioning to a continuous compliance model offers several benefits:
- Enhanced security – By regularly monitoring systems, organizations can identify and mitigate risks more promptly, thereby enhancing overall security.
- Reduced compliance costs – The use of automation in compliance checks reduces the need for extensive manpower and resources, leading to cost savings.
- Improved agility – Continuous compliance enables organizations to adapt more quickly to changes in regulations, maintaining operational efficiency and compliance in a changing landscape.
How Automation Plays a Role in Continuous Compliance
Security automation involves using technology to perform security tasks without human intervention, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing the likelihood of errors.
Automation is a pivotal component in the realm of continuous compliance, offering a more efficient, accurate, and integrated approach to managing compliance tasks by ensuring efficient compliance management, consistency and accuracy, and seamless integration into development and deployment.
Efficient Compliance Management
Automation in continuous compliance translates to the streamlining of routine tasks. By automating processes such as data monitoring, reporting, and compliance checks, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively, focusing on strategic areas rather than routine compliance activities.
Consistency and Accuracy
One of the significant advantages of automation is the reduction in human error. Automated systems provide a consistent approach to compliance processes, ensuring accuracy and reliability in meeting regulatory requirements.
Seamless Integration Into Development and Deployment
The integration of continuous compliance within the CI/CD pipeline is a critical factor in modern software development. This integration ensures that every stage of software development and deployment is compliant, thereby streamlining the development process and embedding compliance into the very fabric of the product lifecycle.
Assessing Your Current Compliance Status
Before embarking on a continuous compliance strategy, a thorough assessment of your organization's current compliance status is essential. This step involves identifying existing gaps in processes and systems and meticulously documenting current policies and procedures. Understanding your organization's standing in terms of regulatory compliance and pinpointing areas for improvement or overhaul is crucial. During this assessment, there are several key areas of focus.
Selection of Tools and Technologies
When selecting tools and technologies for efficient compliance management, it's crucial to prioritize factors such as seamless integration with current systems, scalability to accommodate growth, ease of use, and budget considerations. Opt for a range of solutions that enhance compliance processes. This includes advanced monitoring and data analysis tools, automation software for streamlined operations, security testing applications, and robust cloud platforms.
While examples like the ELK Stack, Ansible, and ZAP offer specific functionalities, broader platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide a comprehensive infrastructure to support diverse compliance requirements. It's essential to align tools with your organization's unique needs and compliance goals, and these examples are just a few of many tool options for compliance management.
Integration of Automated Testing and Monitoring
Incorporate automated testing and monitoring into your IT infrastructure. Regularly conduct automated security tests and use real-time monitoring tools to ensure compliance and address issues promptly.
Continuous Training and Awareness
Implement continuous training and awareness programs for staff to keep them updated on compliance regulations and best practices. This helps ensure everyone understands their role in compliance.
Regular Reviews and Iteration
Periodically review your compliance posture with regular audits and assessments. Adjust and evolve your compliance strategy based on these evaluations to keep up with changing regulations and organizational needs, ensuring a dynamic and effective approach.
Challenges in Transitioning to a Continuous Compliance Model
Transitioning to continuous compliance involves several challenges:
- Complex implementation – Integrating new tools and processes into existing systems can be complex and resource-intensive. Staff may face a steep learning curve adapting to these new technologies and procedures.
- Dependency on technology – Continuous compliance relies heavily on automation and monitoring tools, making any tool failure or limitation a significant concern. Additionally, increased automation can heighten cybersecurity risks, necessitating secure compliance tools.
- Ongoing maintenance and updates – Compliance regulations continually evolve, requiring regular updates to compliance systems. This demands continuous investment in time and resources for maintenance.
- Potential for over-reliance on automation – There's a risk of becoming too dependent on automation, possibly overlooking emerging compliance issues that need human insight. Striking a balance between automation and human oversight is crucial to managing complex compliance situations effectively.
Conclusion
This article highlighted the essential role of continuous compliance and security automation in today's digital world. We've explored adapting to changing standards and incorporating these practices in business and IT. Despite challenges like regulatory shifts and balancing automation with human oversight, pursuing continuous compliance is key, offering benefits such as better security, cost savings, and agility. This journey is more than a regulatory requirement; it's a strategic move for success in a fast-changing, regulated digital environment.
This is an article from DZone's 2023 Enterprise Security Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments