Comprehensive Guide To Troubleshooting IPsec VPN Site-To-Site Connections With PSK on FortiGate Firewalls
Here’s a structured approach to diagnose and resolve common IPsec VPN problems between two sites: "Headquarter" and "Branch".
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeTroubleshooting IPsec VPN Site-to-Site connections on a FortiGate firewall can be challenging due to the complex nature of VPN connections. Here’s a structured approach to diagnose and resolve common IPsec VPN problems between two sites: "Headquarter" and "Branch".
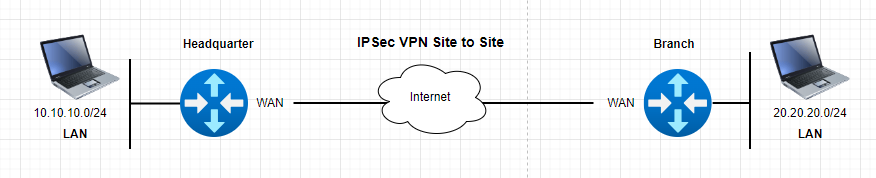
Topology
Step 1: Verify the VPN Configuration
Check Phase 1 and Phase 2 Settings
- Ensure that both phases of the VPN configuration match on both the FortiGate device and the peer or endpoint. Key parameters to check include:
- WAN interface associated with IPSec tunnel
- IKE version (IKEv1 or IKEv2) (IKEv1 has two modes: Main and Aggressive)
- Remote gateway
- Pre-shared key
- Encryption algorithms
- Hash algorithms
- Diffie-Hellman groups
- Phase 2 selectors
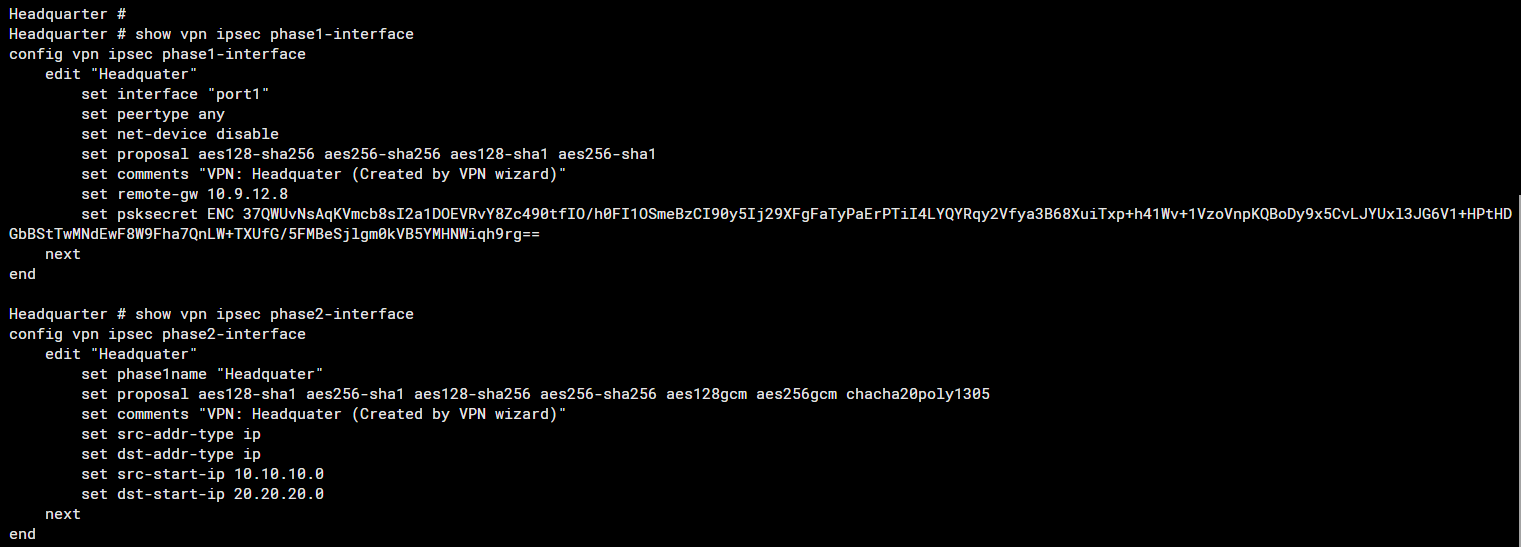
Phase 1 and 2 Configuration on "Headquarter"
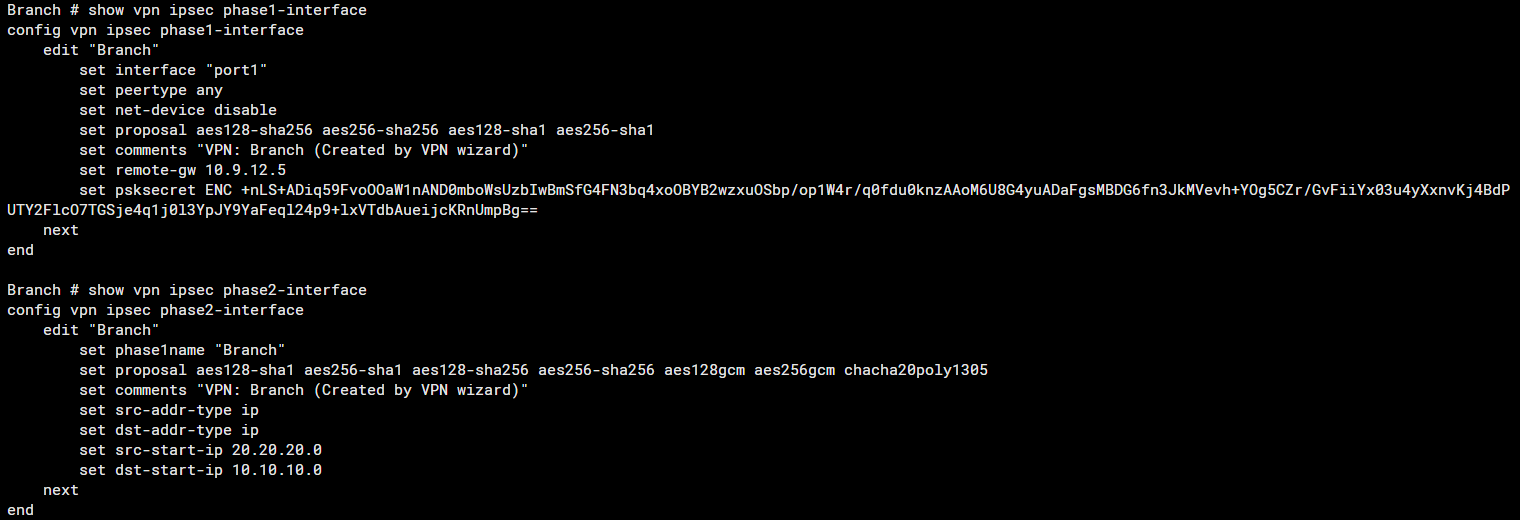
Phase 1 and 2 Configuration on "Branch"
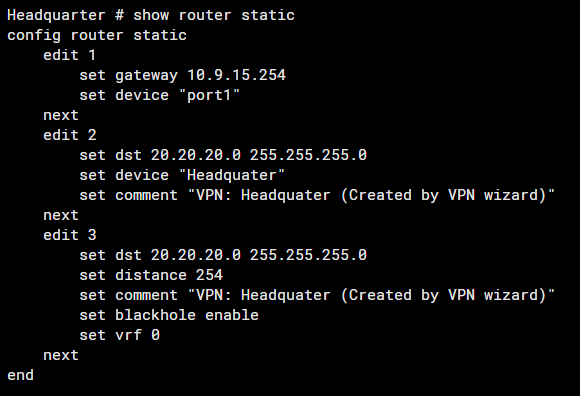
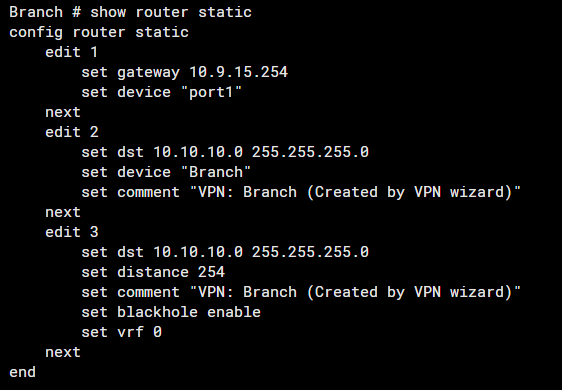
Ensure Static Routes Are Correctly Configured
Note: The command #set device "Headquater" refers to the IPSec tunnel interface.
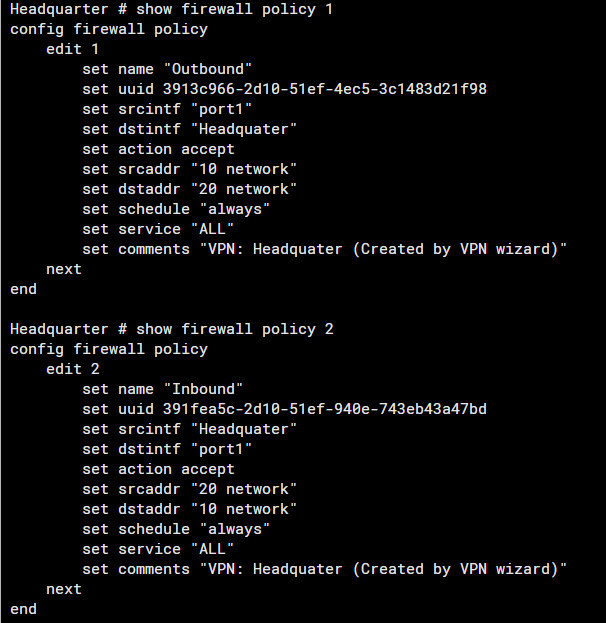
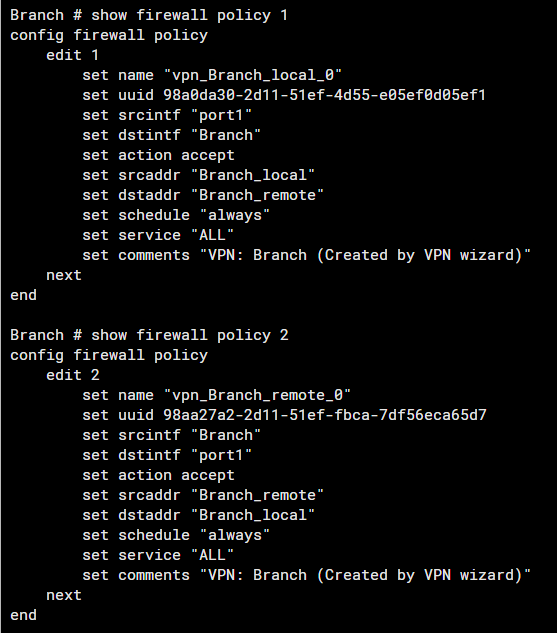
Review Firewall Policies Used for IPsec
- Verify that the policies, Inbound and Outbound are correctly configured to allow traffic from and to the VPN.
- Inspect NAT configuration, as improper NAT rules can interfere with VPN traffic. Ensure that NAT traversal is configured if required.
Step 2: Confirm Security Associations (SAs)
- Check SAs: Use the CLI command
diag vpn ike gatewayto check the status of IKE SAs anddiag vpn tunnel listto view the IPsec SAs. These commands will indicate if the tunnels are up and provide information on their current stage. - Phase 1 checks
# diagnose vpn ike gateway list name <phase1-interface>
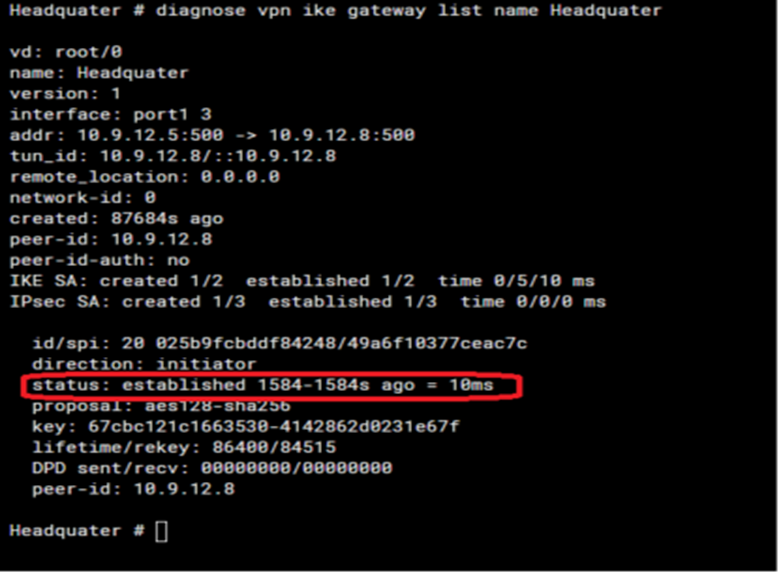
The important field from this particular command is status. The status field has a discrete output that can be either connected or established.
- Established means Phase 1 is up and running.
- Connecting means Phase 1 is down
- Phase 2 checks
If the status of Phase 1 is in an established state, then focus on Phase 2.
#diagnose vpn tunnel list name <phase1-interface>
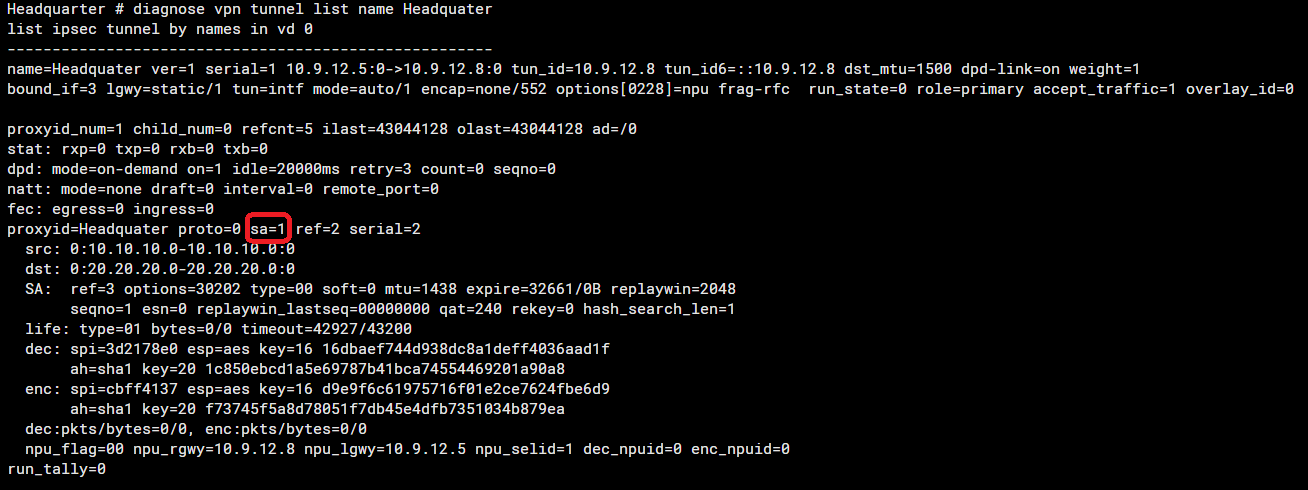
The important field from the particular output is the ‘sa’. SA can have three values:
- sa=0 indicates there is a mismatch between selectors or no traffic is being initiated.
- sa=1 indicates IPsec SA is matching and there is traffic between the selectors.
- sa=2 is only visible during IPsec SA rekey
- Look for mismatches: Any mismatch in SAs between your FortiGate and the peer can cause the tunnel to fail.
- In order to identify errors, run IKE debugging as mentioned in Step 3.
Step 2: Check Network Connectivity
If Phase 1 is not established, conduct further diagnostics to determine the cause. Verify bidirectional connectivity between the VPN gateways is operational.
Validate Connectivity
- Ensure that there is network connectivity between the VPN gateways. This can be checked using tools like ping or traceroute.
# execute ping <remote-gw ip>
# execute traceroute <remote-gw ip>
Note: You could possibly need to have a source ip to ping/traceroute, add
#execute ping-options source <source ip> prior to performing ping and
#execute traceroute-options source <source ip> prior to traceroute
- Inspect routes to ensure that the correct routes are in place on both VPN devices to route traffic through the VPN tunnel.
- Confirm that IKE traffic for port 500 or 4500 is not blocked somewhere along the path, using a packet sniffer.
Capturing IKE Packets
When NAT is not used:
# diag sniffer packet <interface name> "host <remote gw> and udp port 500" 6 0 l
When NAT is used (with NAT traversal enabled under phase1):
# diagnose sniffer packet any 'host <IPSec peer IP> and udp port 500 or udp port 4500' 4 0 l
6: Print header and data from Ethernet of packets (if available) with the interface name. (I usually prefer to use 4 - print header of packets with interface name)0: Unlimited number of packets will be captured.l: Absolute LOCAL time,yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss.ms.
Step 3: Examine IPSec and Debug Logs
Use Log Messages
- FortiGate provides detailed logs that can help identify which part of the VPN connection is failing. Check the event log for any error messages related to IPsec.
Enable Detailed Debug Logs
- If logs are not providing enough information, you can enable detailed debugging for IPsec processes. Use the following CLI commands:
#diagnose vpn ike log-filter clear
#diagnose vpn ike log-filter dst-addr4 <remote-gw ip>
#diagnose debug application ike -1
#diagnose debug console timestamp enable
#diagnose debug enable
Note: Starting from FortiOS v7.4.1, the command diagnose vpn ike log-filter src-addr4 has been changed to diagnose vpn ike log filter loc-addr4.
Check Packet Flow
#diagnose debug flow filter addr <remote-gw ip>
#diagnose debug flow filter proto 17
#diagnose debug flow show function-name enable
#diagnose debug enable
#diagnose debug console timestamp enable
#diagnose debug flow trace start 99
Note: In command #diagnose debug flow filter proto 17
- UDP - 17
- TCP - 6
- ICMP - 1
Remember to turn off debugging after you’re done to avoid filling up the log storage.
#diagnose debug disable
To reset all filters to the defaults:
#diagnose debug reset
Step 4: Additional Checks
- Peer IP changes: If the IP address of the VPN peer has changed, the tunnel will not be established.
-
MTU Issues: Check and adjust MTU settings on VPN interfaces to prevent fragmentation issues that could affect VPN performance.
-
Interface errors/drops:
#fnsysctl ifconfig <ipsec interface> or <wan interface>
Step 5: Consult FortiGate Documentation
- FortiGate documentation: For more specific error codes or messages, refer to the FortiGate documentation or knowledge base articles that provide solutions tailored to particular issues.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting IPsec VPNs involves a careful process of elimination, checking configurations, logs, and network settings. By systematically working through these steps, you can identify and resolve the issues affecting your VPN connection.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments