Handling Sensitive Data: A Primer
Properly securing sensitive customer data is more important than ever. But we’re here to help with a quick data privacy primer.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeProperly securing sensitive customer data is more important than ever. Consumers are increasingly insisting that their data be secured and managed properly. The regulatory environment is also becoming tougher, and business requirements are becoming increasingly complex. The burden is placed on the company and its development teams to meet these requirements while still delighting users.
If that leaves you in a bind, we’re here to help with a quick data privacy primer! First, we’ll help you to understand the various kinds of sensitive customer data and the regulations that apply to it. Next, we’ll guide you in assessing your current handling of that data. Finally, we’ll provide direction on how to properly govern that data.
Learn
The first task is to understand what kind of sensitive customer data you are already handling and what regulations apply to it. Three factors determine which regulations apply to a given set of data:
- The data itself
- Your company’s industry vertical
- The location(s) where your business operates
First, consider the data itself. Depending on the type of data that is being stored in your system, different regulations apply.
Let’s begin with Personal Information (PI). This is perhaps the broadest category of regulated data, referring to nearly anything that is or can be associated with a person. PI is regulated by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Privacy Rights Act (CRPA), NY SHIELD, and others. Examples of this data include:
- IP addresses
- Geolocation information
- Internal ID numbers
- Ethnic or racial origin
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is a subcategory of PI and refers to any data which could be used to distinguish or otherwise determine a person’s identity. Generally speaking, the same regulations which apply to PI also apply to PII, although with differing levels of sensitivity. Examples of PII include:
- Names
- Phone numbers
- Driver’s license or other ID numbers
- Social Security Numbers (SSNs are more highly regulated than other PII)
- Biometric records
Other categories of private consumer data tend to be industry-specific. For example, Protected Health Information (PHI) refers to all “individually identifiable health information.” This is regulated in the US by HIPAA, and is defined as any information which relates to any of the following:
- The individual’s past, present, or future physical or mental health or condition
- The provision of healthcare to the individual
- The past, present, or future payment for the provision of healthcare to the individual
Similarly, Nonpublic Personal Information (NPI) refers to the personally identifiable financial information that is provided by a consumer to a financial institution, and as such is specific to financial service organizations. In the US, NPI is regulated by the Gramm-Leach Bliley Act (GLBA).
Finally, some types of personal information are governed by location-specific regulations. Sensitive Personal Information (SPI) is defined by the CPRA. This refers to data that does not directly identify an individual but may cause harm if made public. Examples include ID numbers, geolocation, account login information, and genetic information.
Private Information is defined by the NY SHIELD Act and applies to any data related to a resident of New York. Additionally, nearly every privacy regulation has some kind of location scope (such as GDPR for the EU, HIPAA for the US, and so on).
This is not an exhaustive list of regulations or categories of sensitive customer data. With this in mind, however, we can see several trends. First, many of these categories overlap with one another. The same data can fall under the scope of multiple regulations and must be handled according to the requirements of all regulations that are relevant to your business. Second, the relevant regulations will heavily depend on your organization’s industry vertical and the locations in which it operates. Finally, even within a given regulation, different data can have differing levels of sensitivity.
With an understanding of the various types of sensitive customer data in mind, we are now ready to begin an assessment process. This assessment will answer the question, “How is my sensitive customer data being handled now?”
Assess
Before determining how sensitive customer data should be handled, it is helpful to take some time to assess how it is currently being handled. To begin, compile a list of customer data that is already being handled and stored. Next, you should carry out two assessments: a technical assessment and a policy assessment
A technical assessment tells you where the data flows through the system. Begin with the moment that data enters the system, and trace it through the various pieces of your application. Make sure to consider the application, service, and data layers. Additionally, note any places where that data exits the system, and make note of where that data goes, such as another application or a business reporting tool. Do this for each piece of sensitive customer data that is currently in the system. As you continue to do this, make note of any inconsistencies or mishandling to address later.
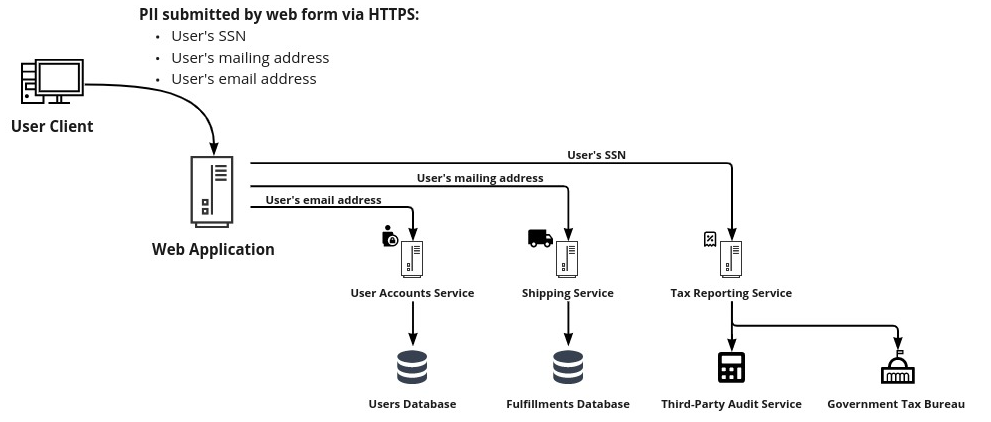
Example: Tracing the flow of user PII through a system
With a policy assessment, you review current policies and controls around data governance. Begin by compiling your organization’s internal documentation around sensitive data and reviewing the written policies and procedures. From there, consider whether these policies adequately cover the types and amount of sensitive data that your company currently handles. Another critical part of this assessment is determining whether these policies are being effectively executed, or if actual governance has diverged from the original intent.
With both assessments in hand, you should be able to confidently describe your organization’s current handling of sensitive customer data. Additionally, you will have identified areas for improvement or areas that require further research. Now, we are ready to define what should be done about your sensitive customer data.
Govern
To properly govern your sensitive customer data, we recommend a three-step process.
- First, determine the regulations which apply to you, and which subsets of data they apply to.
- Second, determine which policies need to apply to each subset of sensitive data.
- Lastly, based on the required policies, design or find a technical solution to implement and reinforce those policies.
Proper technical governance of sensitive customer data protects sensitive data without making it unnecessarily difficult to use. Rather than simply storing it side-by-side with the rest of your data, consider isolating your sensitive data in a zero trust data privacy vault. This approach allows for your sensitive data to be properly governed with its own separate controls. Additionally, your data privacy vault can grow along with the scope of sensitive data your organization handles, allowing for scalability.
If you’re looking to achieve compliance with data privacy regulations in days instead of weeks, one of your options for a dedicated data privacy vault is Skyflow. Skyflow uses a zero trust approach to storing sensitive data of all types. The data is isolated, encrypted, and secure, yet still usable in your business workflows. Granular access policies are available for all data in the vault and are easily defined with the Skyflow Data Governance Engine. All actions are logged and auditable. Skyflow has solutions for FinTech, Healthcare, PII, and more, and it is compliant with privacy regulations worldwide.
Wrap-up
We’ve gone through a three-step approach (Learn. Assess. Govern.) for handling sensitive customer data in your organization. First, we went through the various types of sensitive data and the regulations which apply to them. Next, we described how you can assess how your organization handles sensitive customer data. Finally, we sketched out a flow for properly governing your sensitive customer data. We also considered how an isolated data privacy vault such as Skyflow can help with that.
The landscape of sensitive data governance is continually changing, as new regulations are created and existing ones are strengthened. As such, this process is not something that can just be done once; it must be continually updated as your organization grows and as regulations change.
Published at DZone with permission of Michael Bogan. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments