High-Performance Storage Solutions
Pairing PostgreSQL with fast storage solutions is crucial for optimizing performance, minimizing downtime, and ensuring seamless data access.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreePostgreSQL is a highly popular open-source database due to its rich feature set, robust performance, and flexible data handling. It is used everywhere from small websites to large-scale enterprise applications, attracting users with its object-relational capabilities, advanced indexing, and strong security. However, to truly unleash its potential, PostgreSQL demands fast storage. Its transactional nature and ability to handle large datasets require low latency and high throughput. This is why pairing PostgreSQL with fast storage solutions is crucial for optimizing performance, minimizing downtime, and ensuring seamless data access for demanding workloads.
For flexibility, scalability, and cost optimization, it is preferable to run PostgreSQL on Virtual Machines, especially in development and testing environments. But sometimes, Virtualization introduces an abstraction layer that can lead to performance overhead compared to running directly on bare metal. On the other hand, using just bare metal leads to non-optimal usage of the CPU and storage resources, because one application typically doesn’t fully utilize the bare metal server performance.
In this document, we’ll look at the optimal way to provide high performance to PostgreSQL in a virtualized environment.
With this goal, we are comparing the performance of the vHOST Kernel Target with Mdadm against the SPDK vhost-blk target protected by Xinnor’s xiRAID Opus.
Mdadm, which stands for "Multiple Devices Administration", is a software tool used in Linux systems to manage software RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations. Unlike hardware RAID controllers, mdadm relies on the computer's CPU and software to achieve data redundancy and performance improvements across multiple physical disks.
XiRAID Opus (Optimized Performance in User Space) is a high-performance software RAID engine based on the SPDK libraries, designed specifically for NVMe storage devices.
We are focusing the benchmark on software RAID, as hardware RAID has only 16 PCIe lanes, meaning that by the design the performance is limited to one of a maximum of 4 NVMe drives per controller, which is not sufficient for PostgreSQL applications.
As a testing tool, we employed the pgbench utility and conducted tests on all three built-in scripts: tpcb-like, simple-update, and select-only. The script details are provided in Appendix 2.
Test Setup
Hardware Configuration
- Motherboard: Supermicro H13DSH
- CPU: Dual AMD EPYC 9534 64-Core Processors
- Memory: 773,672 MB
- Drives: 10xKIOXIA KCMYXVUG3T20
Software Configuration
- OS: Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS
- Kernel: Version 5.15.0-91-generic
- xiRAID Opus: Version xnr-1077
- QEMU Emulator: Version 6.2.0
RAID Configuration
Two RAID groups (4+1 configuration) were created utilizing drives on 2 independent NUMA nodes. The stripe size was set to 64K. A full RAID initialization was conducted prior to benchmarking.
Each RAID group was divided into 7 segments, with each segment being allocated to a virtual machine via a dedicated vhost controller.
Summary of Resources Allocated
- RAID Groups: 2
- Volumes: 14
- vhost Controllers: 14
- VMs: 14, with each using segmented RAID volumes as storage devices.
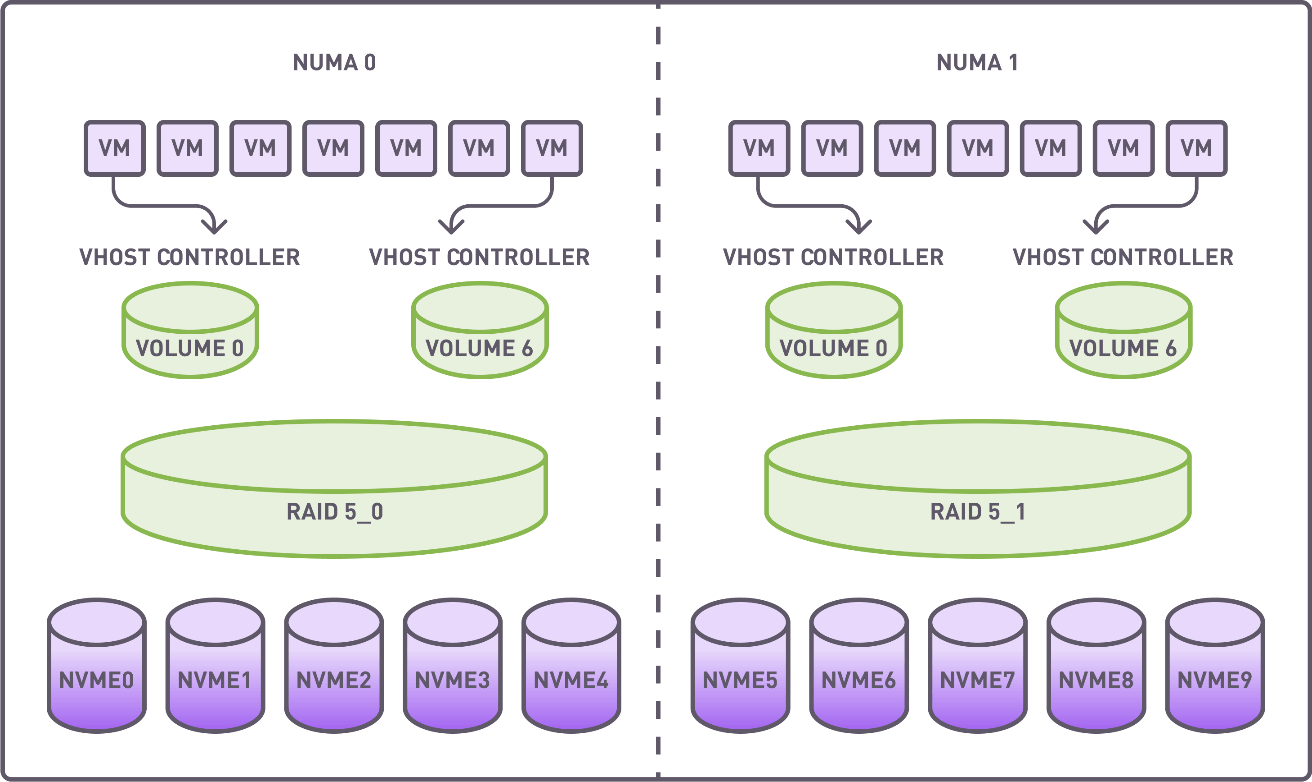
Distribution of virtual machines, vhost controllers, RAID groups, and NVMe drives.
During the creation of mdraid, volumes, and vhost targets, assignment to specific CPU cores was not conducted because not supported. Nevertheless, virtual machines continued to operate on specific cores.
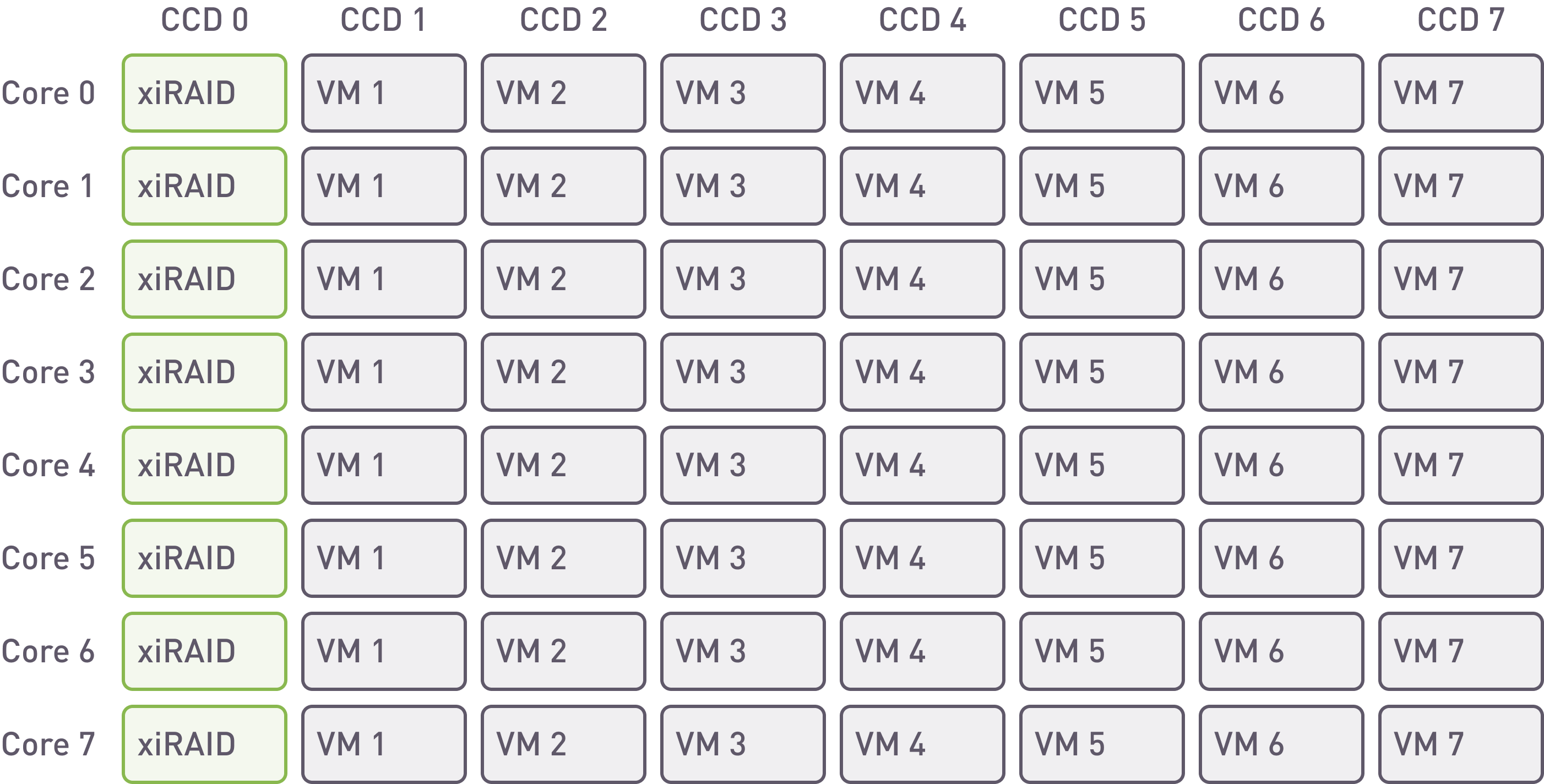
xiRAID. Placement of the array and VMs on cores.
With xiRAID it is possible to assign the RAID engine to specific cores. In this example, we are using 8 cores for any NUMA node. Such placement allows for separating infrastructure and database workloads and to isolate VM loads from each other.
This feature is not available on MDRAID, so the application must share the core resources with the RAID engine.
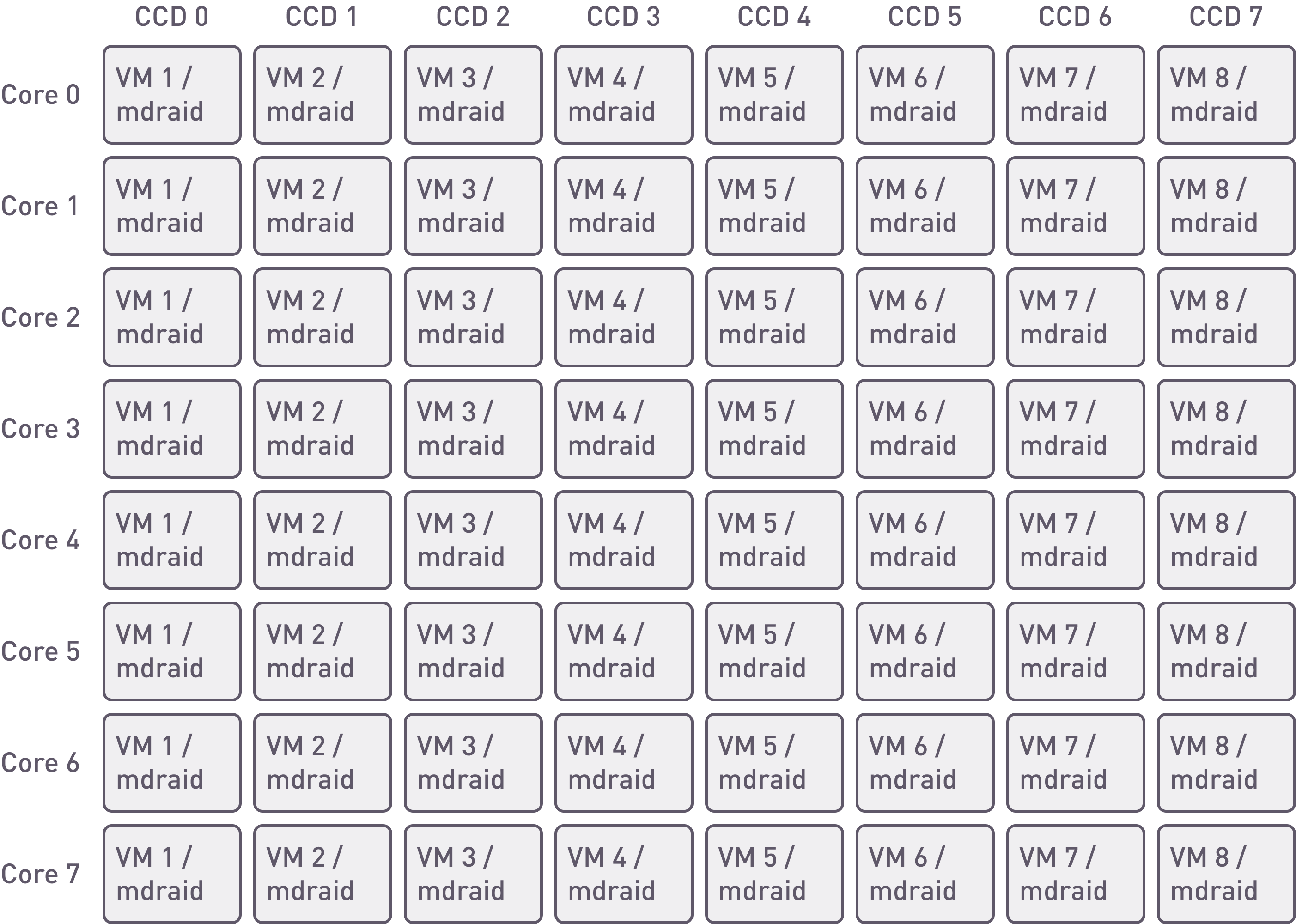
mdraid. Placement of the array and VMs on cores.
Virtual Machine Configuration
CPU Allocation: 8
-cpu host -smp 8
QEMU Memory Configuration
- Memory Allocation: Each VM is provisioned with 32 GB of RAM via Hugepages. Memory is pre-allocated and bound to the same NUMA node as the allocated vCPUs to ensure efficient CPU-memory interaction.
-m 32G -object memory-backend-file,id=mem,size=32G,mem-path=/dev/hugepages,share=on,prealloc=yes,host-nodes=0,policy=bind- Operating System: VMs run Debian GNU/Linux 12 (Bookworm)
- PostgreSQL Version: 15
PostgreSQL Configuration
apt-get install postgresql-15 // installing PostgreSQL 15
cd /etc/postgresql/15/main/
sed -i 's|/var/lib/postgresql/15/main|/test/postgresql/15/main|g' postgresql.conf // configuring the folder for the data
sed -i -e "s/^#\?\s*listen_addresses\s*[=]\s*[^\t#]*/listen_addresses = '127.0.0.1'/" postgresql.conf
sed -i -e "/^max_connections/s/[= ][^\t#]*/ = '300'/" postgresql.conf // increasing the number of connections up to 300
apt-get install xfsprogs
mkdir /test
mkfs.xfs /dev/vda -f
mount /dev/vda /test -o discard,noatime,largeio,inode64,swalloc,allocsize=64M -t xfs
cp -rp /var/lib/postgresql /test/
service postgresql restartConfiguring the folder for the data:
sudo -u postgres createdb test
sudo -u postgres pgbench -i -s 50000 testWe created and initialized the database for testing purposes. It is important to choose the scaling correctly so that all data does not fit into the RAM.
Testing
We conducted tests while varying the number of clients and reported in this document only those where we achieved the maximum stable results. To adjust the number of clients, we selected the following values for the parameter -c (number of clients simulated, equal to the number of concurrent database sessions): 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000. For all script types, we reached a plateau of 100 clients.
As best practice, we fixed the parameter -j (number of worker threads within pgbench*) equal to the number of VM cores.
* Using more than one thread can be helpful on multi-CPU machines. Clients are distributed as evenly as possible among available threads.
The tests appear as follows:
sudo -u postgres pgbench -j 8 -c 100 -b select-only -T 200 test
sudo -u postgres pgbench -j 8 -c 100 -b simple-update -T 200 test
sudo -u postgres pgbench -j 8 -c 100 -T 200 testWe conducted the test three times and recorded the average results across all virtual machines. Additionally, we performed select-only tests in degraded mode, as this script generates the maximum load on reading, enabling an assessment of the maximum impact on the database performance.
During the test, we monitored the array performance using the iostat utility. The total server performance comprises the sum of the performance of all machines (14 for xiRAID Opus and 16 for mdraid).
Select-Only Test Results
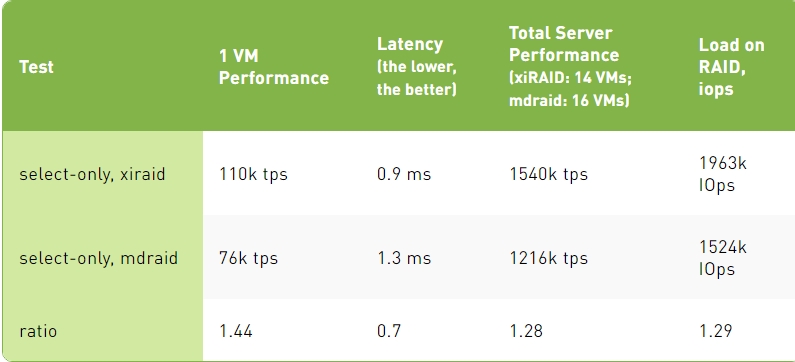
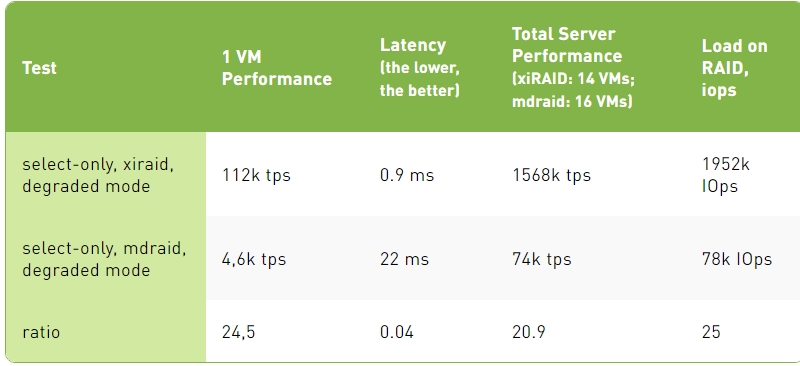
Select-Only Test Results, Degraded Mode
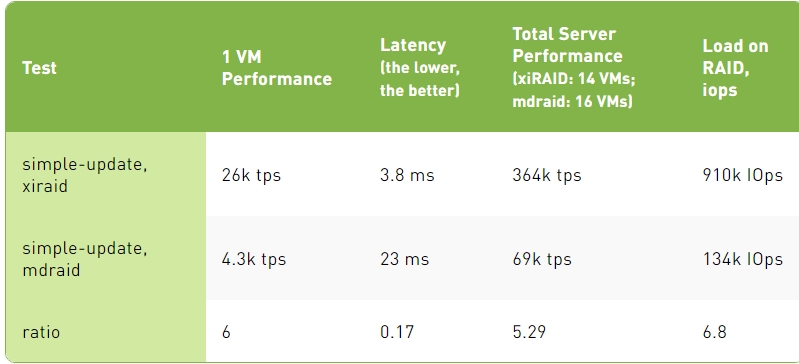
Simple-Update Test Results
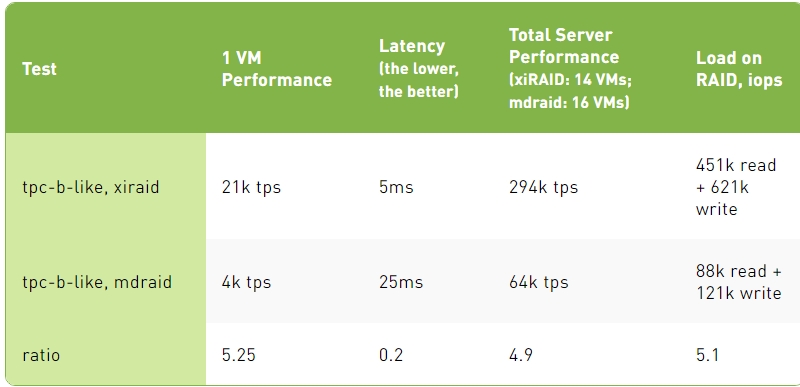
TPC-B-Like Test Results
Conclusion
1. In select-only, with all the drives in the RAID operating properly, xiRAID Opus provides 30-40% better transactions per second than mdraid. Mdraid is nearing its maximum capabilities, and further scaling (by increasing the number of cores for virtual machines) would become challenging. This is not the case for xiRAID. The main reason for such a difference is the fact that xiRAID Opus enables the vhost target to run on a separate CCD.
When comparing different protection schemes, we cannot stop at measuring performance in normal operations. Indeed, RAID protection is needed to prevent data loss in case of one or more drive failures. In this situation (degraded mode), maintaining high performance is critical to avoid downtime for the database users.
When comparing performance in degraded mode, mdraid experiences a significant drop in performance, leading to over 20X times slower performance than xiRAID. In other terms, with MDRAID, users will be waiting for their data and this situation can lead to business losses (think about an online travel agency or a trading company).
2. When it comes to writing data to the database, each write of small blocks generates RAID calculations. In this situation, mdraid's performance is six times worse than xiRAID Opus.
3. The TPC-B Like script is more complex than the simple update and consumes more CPU resources, which again slows down mdraid on write operations. In this case, xiRAID outpaces mdraid by five times.
4. In conclusion, xiRAID provides great and stable performance to multiple VMs.
This means that applications will be able to get access to their data without any delay, even in case of drive failures or extensive write operations.
Furthermore, the scalability of xiRAID on VMs allows the system admin to consolidate the number of servers needed for large/multiple Database deployments. This benefit oversimplifies the storage infrastructure while providing great cost savings.
Appendix 1. mdraid Configuration
md0 : active raid5 nvme40n2[5] nvme45n2[3] nvme36n2[2] nvme46n2[1] nvme35n2[0]
12501939456 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [5/5] [UUUUU]Bitmaps disabled
cat /sys/block/md0/md/group_thread_cnt
16
Vhost target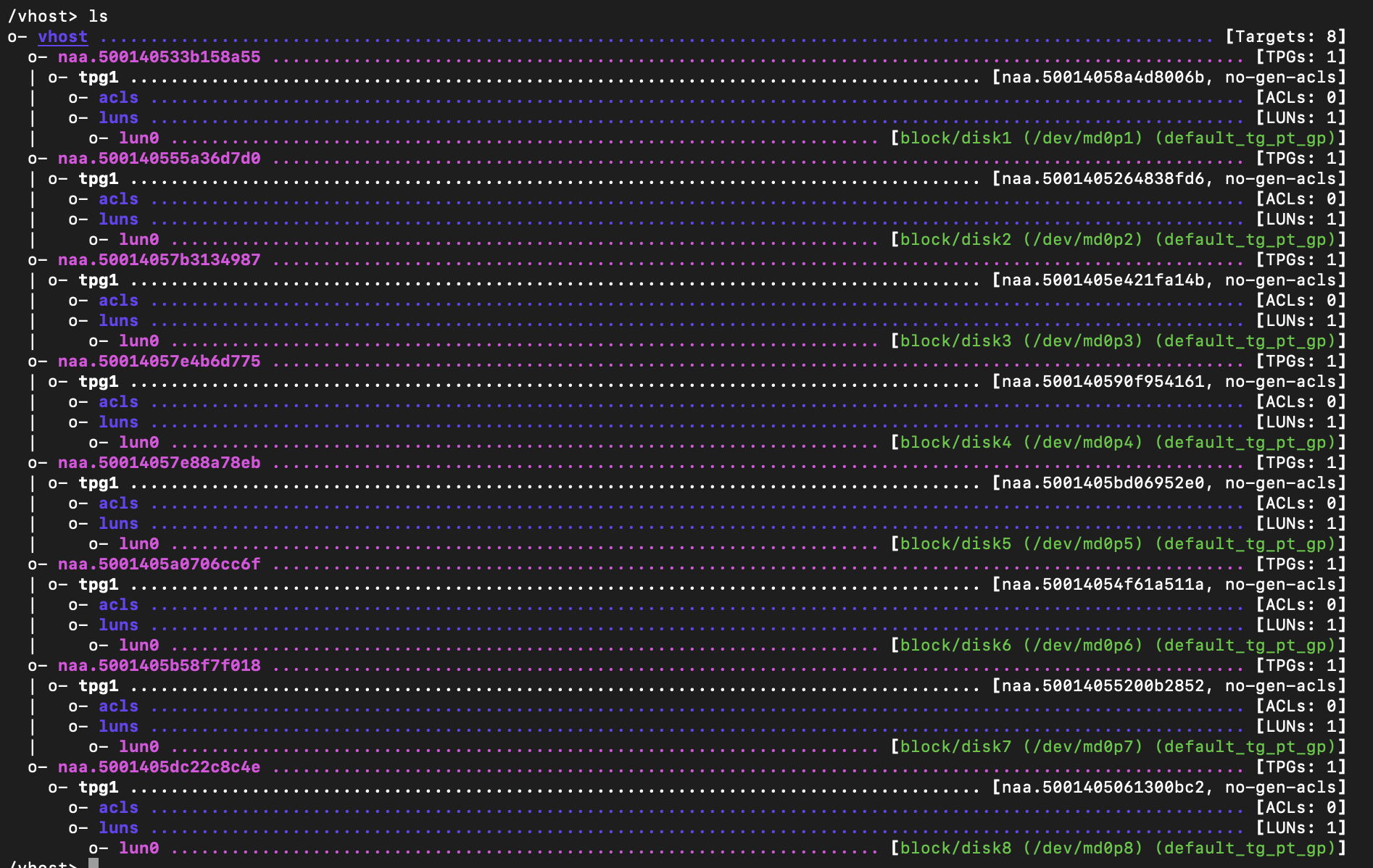
Example Code for Launching VMs
taskset -a -c $CPU qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -smp 8 -cpu host -m 32G -drive file=$DISK_FILE,format=qcow2 --nographic \
-device vhost-scsi-pci,wwpn=naa.5001405dc22c8c4e,bus=pci.0,addr=0x5Published at DZone with permission of Sergey Platonov. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments