If Software Quality Is Everybody’s Responsibility, So Is Failure
When bugs slip through, or products fail to meet expectations, testers are the ones blamed. However, taking a closer look, failure extends beyond any one discipline.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn many large organizations, software quality is primarily viewed as the responsibility of the testing team. When bugs slip through to production, or products fail to meet customer expectations, testers are the ones blamed. However, taking a closer look, quality — and likewise, failure — extends well beyond any one discipline.
Quality is a responsibility shared across an organization. When quality issues arise, the root cause is rarely something testing alone could have prevented. Typically, there were breakdowns in communication, unrealistic deadlines, inadequate design specifications, insufficient training, or corporate governance policies that incentivized rushing.
In other words, quality failures tend to stem from broader organizational and leadership failures. Scapegoating testers for systemic issues is counterproductive. It obscures the real problems and stands in the way of meaningful solutions to quality failings.
Testing in Isolation
In practice, all too often, testing teams still work in isolation from the rest of the product development lifecycle. They are brought in at the end, given limited information, and asked to validate someone else’s work. Under these conditions, their ability to prevent defects is severely constrained.
For example, without access to product requirement documents, test cases may overlook critical functions that need validation. With short testing timelines, extensive test coverage further becomes impossible. Without insight into design decisions or access to developers, some defects found in testing prove impossible to diagnose effectively.
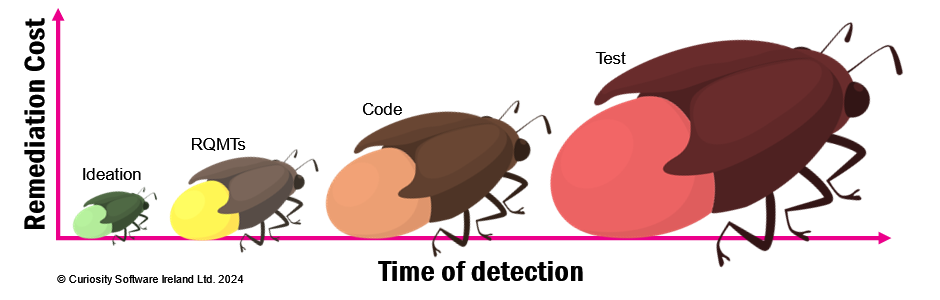
Testers are often parachuted in when the time and cost of repairing a defect has grown to be unfeasible.
In this isolated model, testing serves as little more than a final safety check before release. The burden of quality is passed almost entirely to the testers. When the inevitable bugs still slip through, testers then make for easy scapegoats.
Who Owns Software Quality?
In truth, responsibility for product quality is distributed across an organization. So, what can you do?

Quality is everyone’s responsibility. Image sources: Kharnagy (Wikipedia), under CC BY-SA 4.0 license, combined with an image from Pixabay.
- Executives and leadership teams — Set the tone and policies around quality, balancing it appropriately against other priorities like cost and schedule. Meanwhile, provide the staffing, resources, and timescale needed for a mature testing effort.
- Product Managers — Gather user requirements, define expected functionality, and support test planning.
- Developers — Follow secure coding practices, perform unit testing, enable automated testing, and respond to defects uncovered in testing.
- User experience designers — Consider quality and testability during UX design. Conduct user acceptance testing on prototypes.
- Information security — Perform security reviews of code, architectures, and configurations. Guide testing-relevant security use cases.
- Testers — Develop test cases based on user stories, execute testing, log defects, perform regression test fixes, and report on quality to stakeholders.
- Operations — Monitor systems once deployed, gather production issues, and report data to inform future testing.
- Customers — Voice your true quality expectations, participate in UAT, and report real-world issues once launched.
As this illustrates, no one functional area owns quality alone. Testers contribute essential verification, but quality is truly everyone’s responsibility.
Governance Breakdowns Lead to Quality Failures
In a 2023 episode of the "Why Didn’t You Test That?" podcast, Marcus Merrell, Huw Price, and I discussed how testing remains treated as a “janitorial” effort and cost center, and how you can align testing and quality.
When organizations fail to acknowledge the shared ownership of software quality, governance issues arise that enable quality failures:
- Unrealistic deadlines — Attempting to achieve overly aggressive schedules often comes at the expense of quality and sufficient testing timelines. Leadership teams must balance market demands against release readiness.
- Insufficient investment — Success requires appropriate staffing and support for all areas that influence quality. These range from design and development to development to testing. Underinvestment leads to unhealthy tradeoffs.
- Lack of collaboration — Cross-functional coordination produces better quality than work done in silos. Governance policies should foster collaboration across product teams, not hinder it.
- Misaligned priorities — Leadership should incentivize balanced delivery, not just speed or cost savings. Quality cannot be someone else’s problem.
- Lack of transparency — Progress reporting should incorporate real metrics on quality. Burying or obscuring defects undermines governance.
- Absence of risk management — Identifying and mitigating quality risks through appropriate action requires focus from project leadership. Lacking transparency about risk prevents proper governance.
When these governance breakdowns occur, quality suffers, and failures follow. However, the root causes trace back to organizational leadership and culture, not solely the testing function.
The Costs of Obscuring Systemic Issues
Blaming testers for failures caused by systemic organizational issues leads to significant costs:
- Loss of trust — When testers become scapegoats, it erodes credibility and trust in the testing function, inhibiting their ability to advocate for product quality.
- Staff turnover — Testing teams experience higher turnover when the broader organization fails to recognize their contributions and value.
- Less collaboration — Other groups avoid collaborating with testers perceived as bottlenecks or impediments rather than partners.
- Reinventing the wheel — Lessons from past governance breakdowns go unlearned, leading those issues to resurface in new forms down the line.
- Poorer customer experiences — Ultimately, obscuring governance issues around quality leads to more negative customer experiences that damage an organization’s reputation and bottom line.
Taking Ownership of Software Quality
Elevating quality as an organization-wide responsibility is essential for governance, transparency, and risk management. Quality cannot be the burden of one isolated function, and leadership should foster a culture that values quality intrinsically, rather than viewing it as an afterthought or checkbox.
To build ownership, organizations need to shift testing upstream, integrating it earlier into requirements planning, design reviews, and development processes. It also requires modernizing the testing practice itself, utilizing the full range of innovation available: from test automation, shift-left testing, and service virtualization, to risk-based test case generation, modeling, and generative AI.
With a shared understanding of who owns quality, governance policies can better balance competing demands around cost, schedule, capabilities, and release readiness. Testing insights will inform smarter tradeoffs, avoiding quality failures and the finger-pointing that today follows them.
This future state reduces the likelihood of failures — but also acknowledges that some failures will still occur despite best efforts. In these cases, organizations must have a governance model to transparently identify root causes across teams, learn from them, and prevent recurrence.
In a culture that values quality intrinsically, software testers earn their place as trusted advisors, rather than get relegated to fault-finders. They can provide oversight and validation of other teams’ work without fear of backlash. And their expertise will strengthen rather than threaten collaborative delivery.
With shared ownership, quality ceases to be a “tester problem” at all. It becomes an organizational value that earns buy-in across functional areas. Leadership sets the tone for an understanding that if quality is everyone’s responsibility — so too is failure.
Published at DZone with permission of Rich Jordan. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments