How To Manage Redis Cluster Topology With Command Line
Understanding and managing Redis cluster topology is crucial. Learn commands are extremely helpful in managing and troubleshooting Redis cluster topology.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeManual intervention is often necessary to understand and manage the current topology of a Redis cluster. This article covers essential commands for interacting with and managing the Redis cluster, along with retrieving its state information.
CLUSTER INFO
This command gives you an overview of your Redis cluster, including details about key distribution, participating nodes, cluster size, and message statistics.

CLUSTER NODES
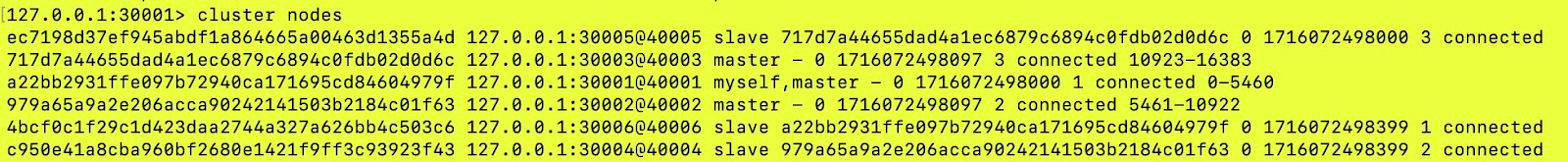
With CLUSTER NODES, find information about the nodes that are a part of the Redis cluster.
Questions
- How many nodes are part of the cluster?
- The total number of rows shows the number of nodes that are a part of this Redis cluster. The cluster above has 6 nodes.
- What are the IPs or ports on which these nodes are present?
- In this IP is 127.0.0.1 and port is 30005 for this node.

- Is a node primary or replica?
- One of the primary nodes in the cluster above:
![]()
- One of the replica nodes in the cluster above:
![]()
- One of the primary nodes in the cluster above:
- What’s the unique node ID of the node?
- In the above row,
717d7a44655dad4a1ec6879c6894c0fdb02d0d6cis the unique ID of the node.
- In the above row,

- Is the node connected or not?
- The string “connected” in the picture below shows the node is connected.
![]()
- The string “disconnected” in the picture below shows the node is disconnected. Also, the status is “fail”.
![]()
- The string “connected” in the picture below shows the node is connected.
CLUSTER SLOTS
This command provides the mapping of the hash slots to cluster nodes so that we can identify which slots are served with which primary and replica nodes.

The output displays information about each hash slot in the cluster. Notably, the first node ID listed for each slot corresponds to the primary node holding that slot's data, while the second node ID represents its replica.
CLUSTER FORGET <node_id>
A troubled node within your Redis cluster can lead to slow response times for client requests. To maintain optimal performance and avoid latency spikes, the CLUSTER FORGET command allows you to proactively remove the problematic node from the cluster, directing client requests to healthy nodes.
- Note: You need to run this command on all the remaining nodes so they update their own copy topology (nodes table) which is maintained on each node. This can be accomplished by running a script that can loop over all remaining nodes (except the one that needs to be removed).
for port in {30001..30006}; do
# Run the CLUSTER FORGET command for each node
redis-cli -p $port CLUSTER FORGET $NODE_ID
doneBefore removing the node:
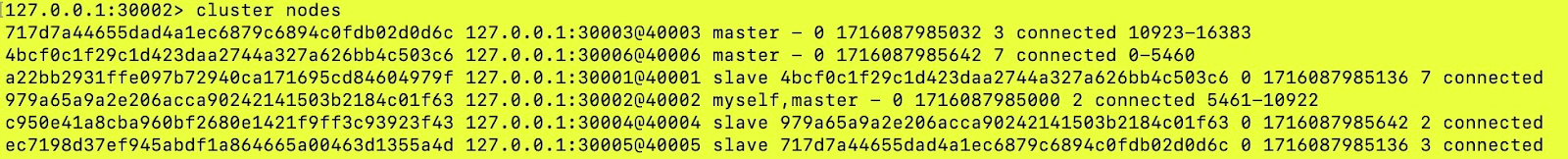
We can see the node with the id 717d7a44655dad4a1ec6879c6894c0fdb02d0d6c and port 30003 is present in the cluster.
Now we can run a script like this:
NODE_ID="717d7a44655dad4a1ec6879c6894c0fdb02d0d6c"
for port in {30001..30006}; do
redis-cli -p $port CLUSTER FORGET $NODE_ID
doneAfter running the script:
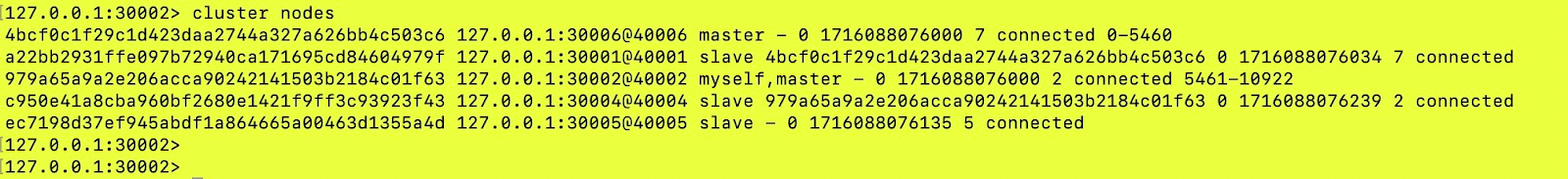
We can now see the node with the id 717d7a44655dad4a1ec6879c6894c0fdb02d0d6c and port 30003 is not present and hence not a part of the cluster.
- Note: This Redis node with id
717d7a44655dad4a1ec6879c6894c0fdb02d0d6cand port 30003 is still running, but not a part of the cluster anymore.
CLUSTER MEET <ip> <port>
When your Redis cluster needs to grow, the CLUSTER MEET command comes in handy. It lets you seamlessly add new nodes to distribute the workload. Additionally, if you previously removed a node due to problems (as we did above using CLUSTER FORGET), you can use CLUSTER MEET to reintroduce it to the cluster once the issues are fixed.
Before running the cluster meet (node with port 30003 is not a part of the cluster):
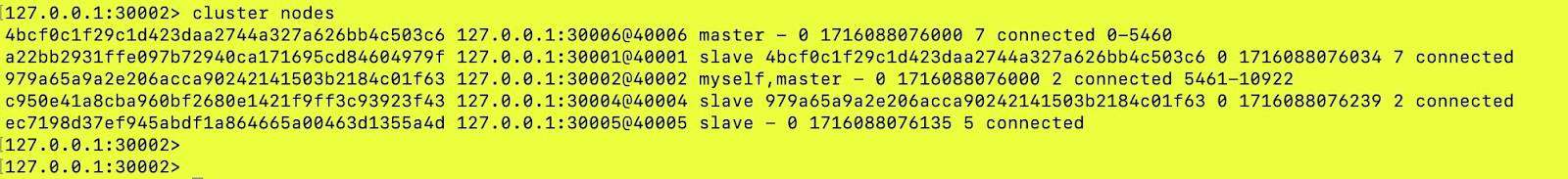
Run the command:

After running the command:

We can see that the node with port 30003 is again a part of the cluster now.
CLUSTER REPLICATE <primary_node_id>
Expanding a Redis cluster involves not just adding nodes but also configuring them for high availability. This command helps us achieve that by promoting a new node to become a replica of an existing node (identified by its ID). This ensures data redundancy and allows clients to access replicas if the primary node fails.
References
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.




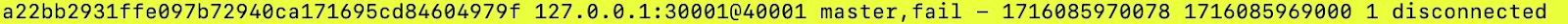
Comments