Practical Use Cases With Terraform in Network Automation
Terraform is a powerful tool that has become essential to modern engineering. Let's dive in and explore its many benefits!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the past, managing network infrastructures was a tedious task that involved manual configuration of devices using console cables and deployment of configurations one machine at a time. However, with the help of automation and tools like Terraform, network engineers can now work more efficiently by saving time and avoiding manual tasks through scripting and large-scale automation.
Terraform is a powerful tool that has become essential to modern engineering. It comes with a rich set of features that network engineers can leverage to their advantage and save time on other tasks. This article is a treasure trove of information on Terraform, so let's dive in and explore its many benefits!
Challenges for Network Engineers
Various technological advancements are constantly disrupting our digital society. However, we need to join the movement of early adopters, innovators, and tech evangelists, such as AI, machine learning, and big data to keep up with the pace of change.
As innovations emerge, user demand increases, making it challenging to manage network infrastructure using outdated methods." The network remains the backbone of our digital economy, network engineers have to adapt to keep our digital society connected and infrastructures resilient to all the changes that may come at times.
Network engineers need to be prepared for any challenges and changes that may arise, and the ability to adapt quickly is crucial.
A New Opportunity in Modern Network Engineering
Automation has become an integral part of modern networking. With the help of powerful tools like Terraform, what would have taken 5 days to achieve can now be done in just an hour. For those who are not familiar with Terraform, it is an open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool developed by HashiCorp. It enables users to define and provision infrastructure resources using a declarative configuration language. A declarative language is a programming language or syntax that focuses on describing the desired outcome or end state, rather than specifying the step-by-step process to achieve it.
Key features:
- Multicloud support: it supports the major cloud providers such as AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, and meraki, a great opportunity to manage different cloud environments thanks to a single tool.
- Declarative configuration: HCL (HashiCorp configuration language) is the declarative language used by Terraform to define the desired state of infrastructure resources.
- Infrastructure as code: infrastructure automation is performed through the use of code
- Modularity and reusability: If you are a fan of space, the Falcon rocket is currently the most powerful and reusable in the world. The same applies to Terraform, where configurations can be organized into reusable modules by encapsulating logic and resources.
Where Does Terraform Fit into Network Automation?
Terraform plays a crucial role in automation, here is where it fits:
- Infrastructure provisioning: Terraform is used for infrastructure provisioning, which involves the provision of network infrastructures such as routers, switches, and load balancers. Network engineers can use a Terraform configuration file to define the desired state of these infrastructures, and Terraform will handle the configuration of resources across different environments, whether it's on-premises or in the cloud.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Terraform considers network infrastructure as code, an opportunity for network engineers to define and manage network configurations using version-controlled files, and this is where automation is enhanced.
- Change management and version control: Terraform is a tool that allows for effective change management by providing a clear view of proposed infrastructure changes through execution plans. The task of network engineers is to review and approve these changes before applying them. Additionally, Terraform configuration files can be stored in a version control system such as Git, which enables teams to track changes over time.
Practical Use Cases
Infrastructure Provisioning
There are various use cases in network automation, let’s focus on 3 short use case snippets.
Let’s write a short snippet for Infrastructure provisioning, in the script we set up an AWS environment including a VPC, subnets, an Internet Gateway, route tables, and a couple of EC2 instances across two availability zones for high availability.
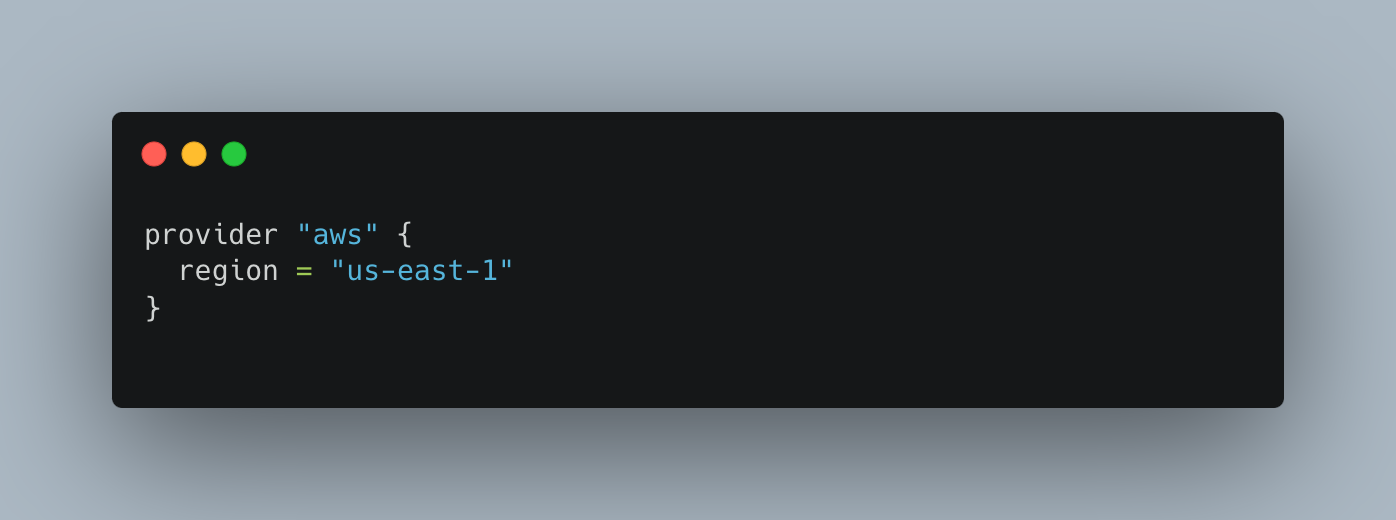
Provider Configuration
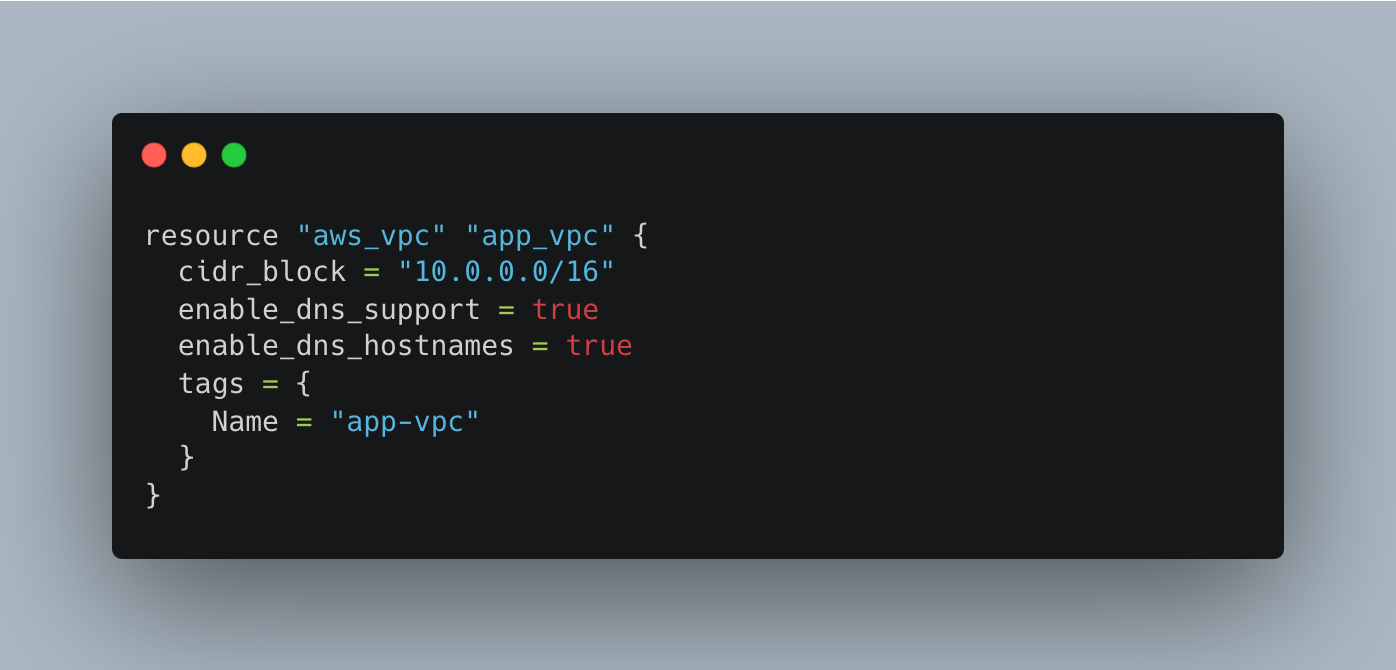
Define the VPC
Subnets

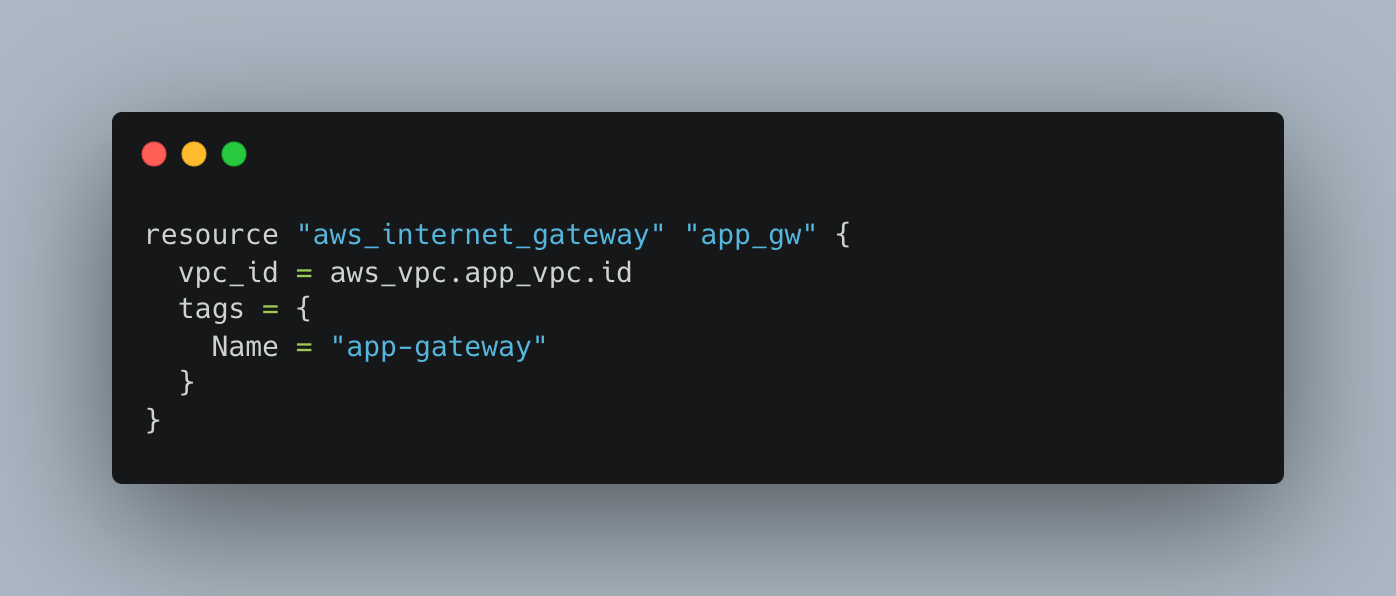
Internet Gateway
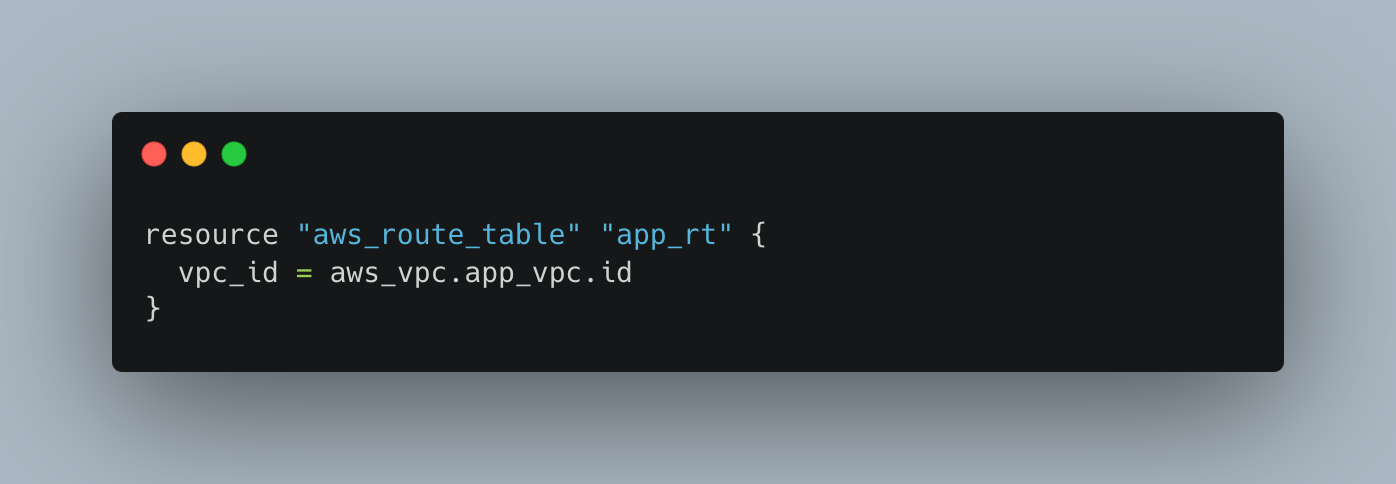
Route Table
**All three use cases have show snippets, but the scripts may still be lengthy in production.
The Terraform script defines the exact configuration for VPCs, subnets, routing tables, and EC2 instances. This ensures consistent deployments and reduces configuration drift and errors.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)

Create a New VPC
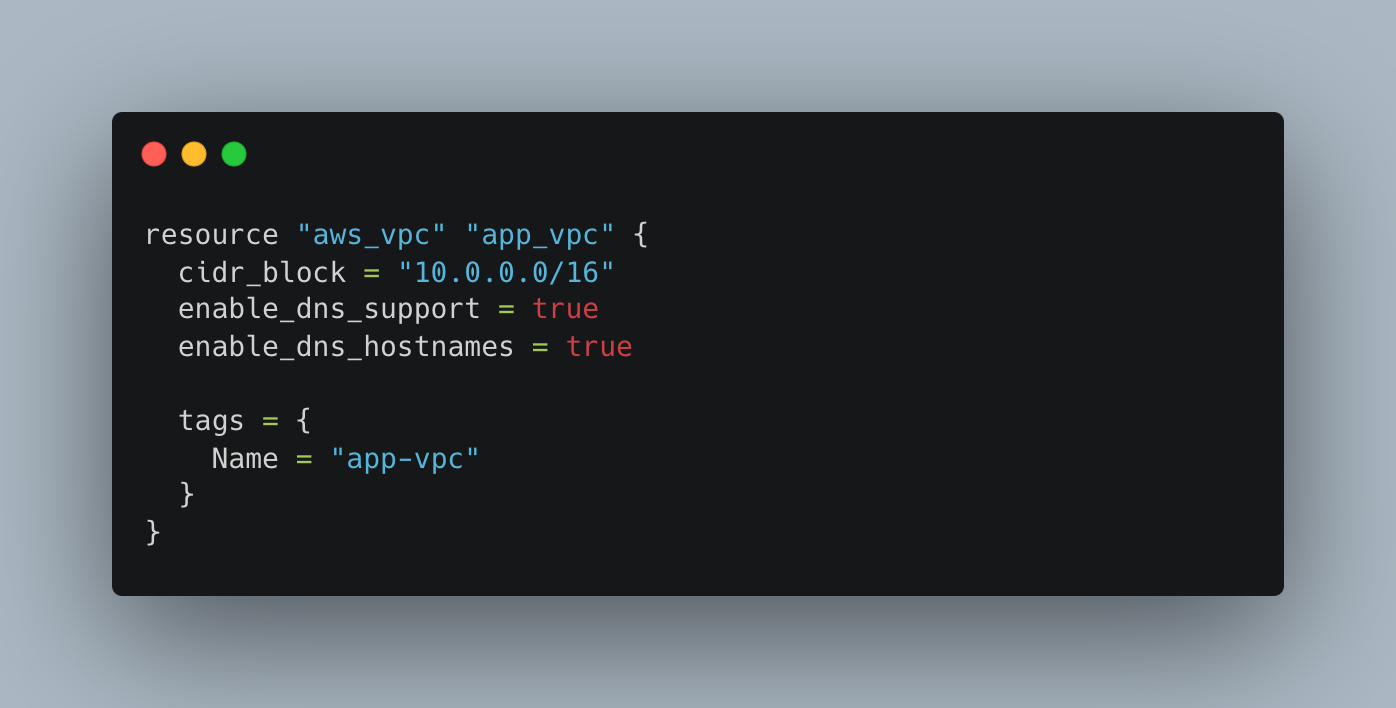
Create Subnets
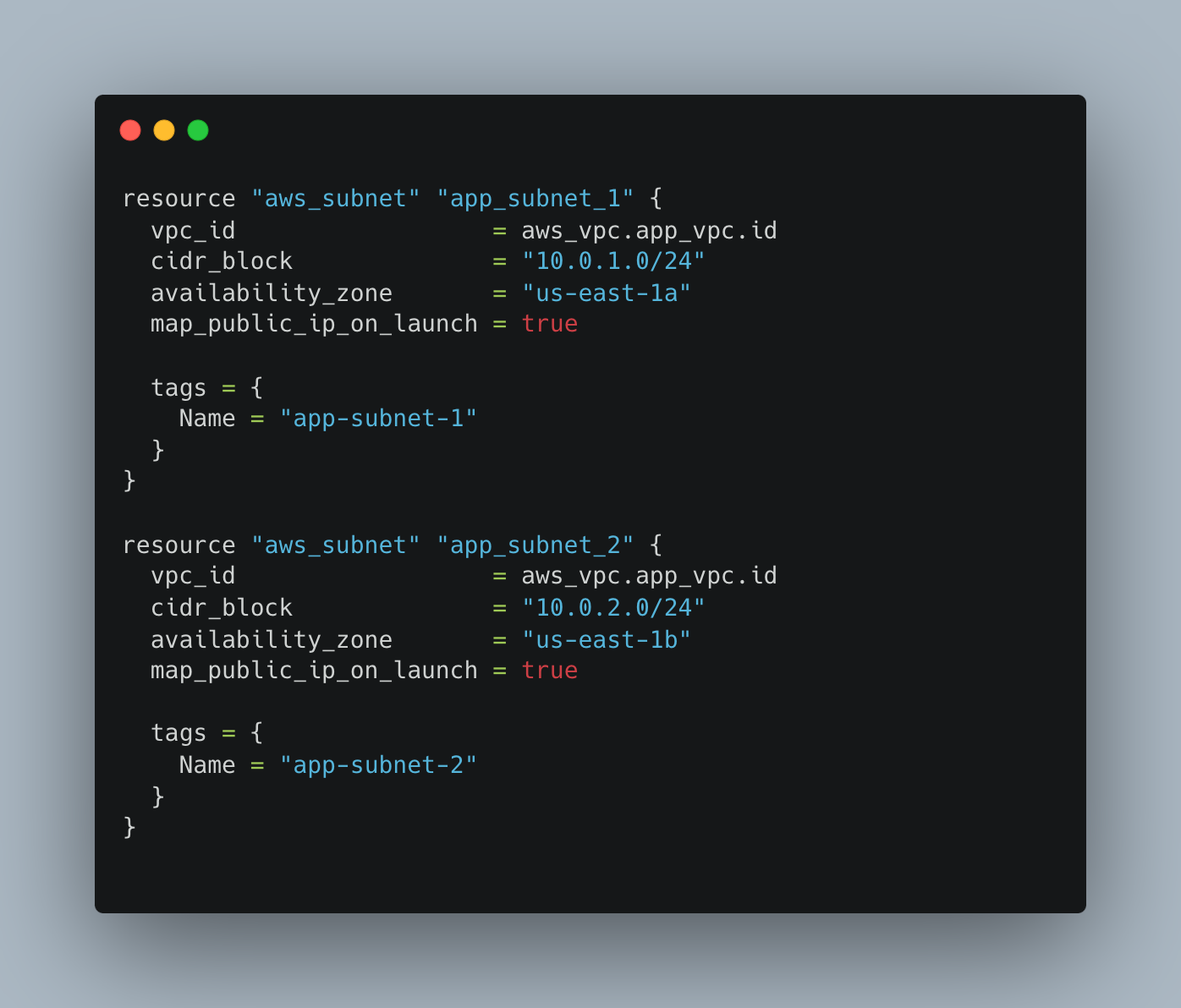
Internet Gateway for the VPC
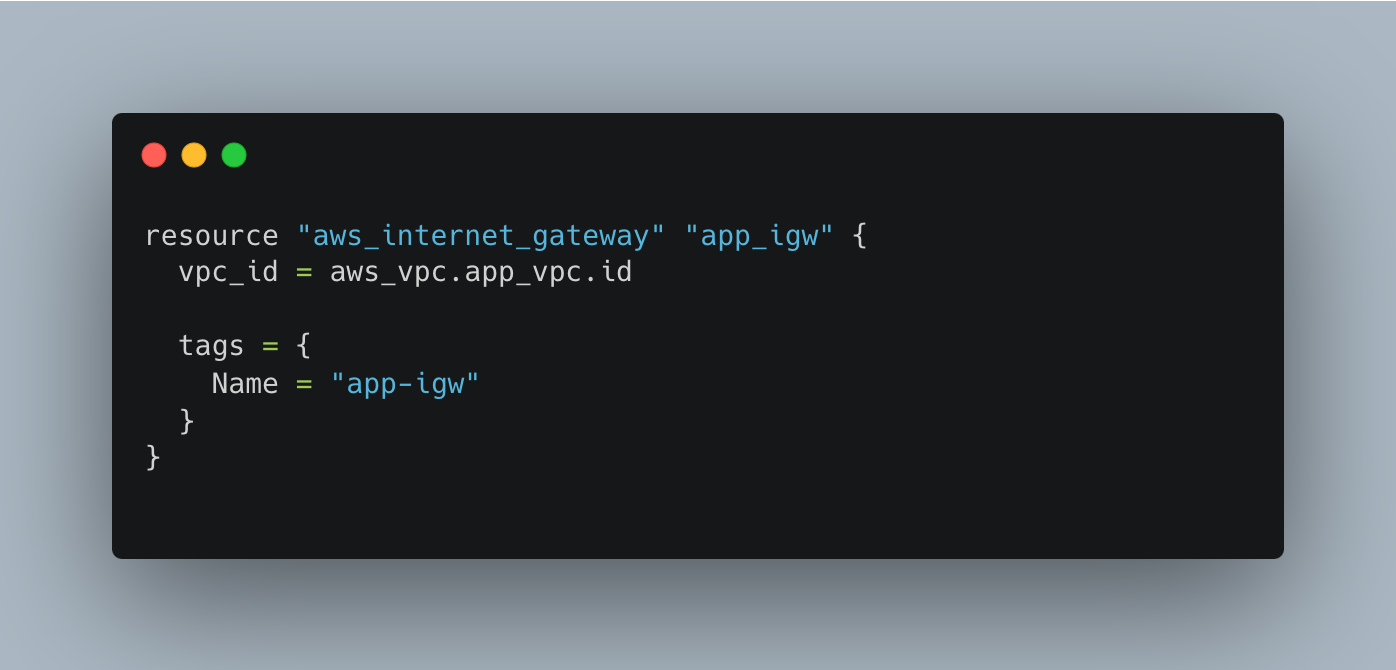
Route Table
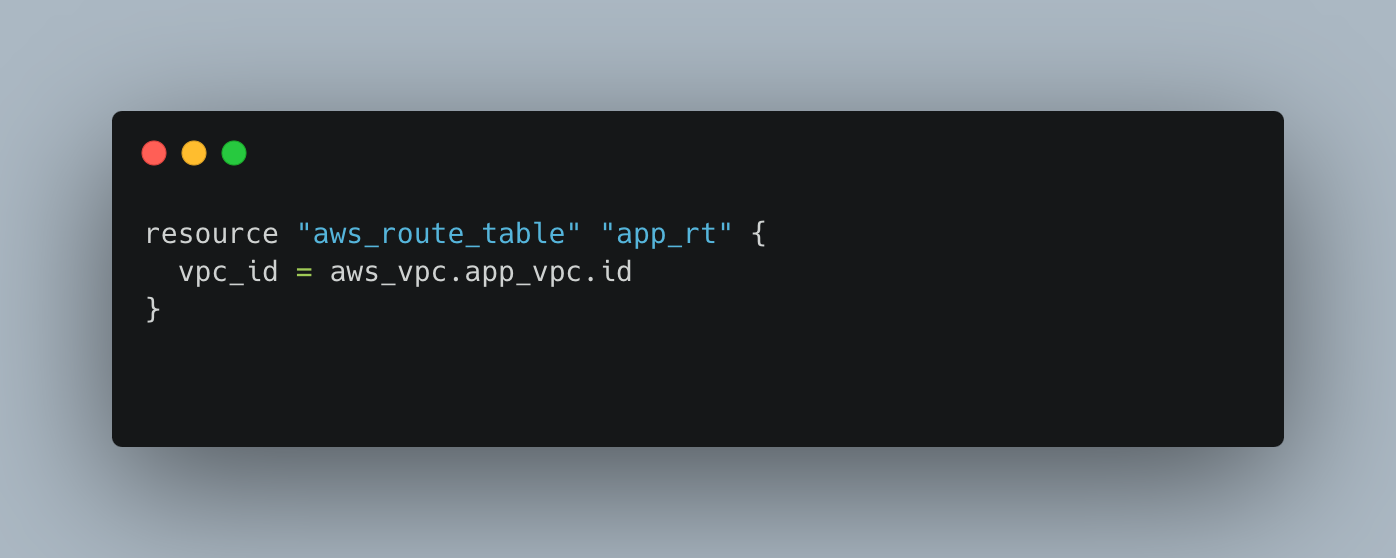
Terraform is an excellent example of Infrastructure as Code (IaC). It enables developers and operations teams to manage and provision infrastructure through code, resulting in quicker deployment and management processes and fewer manual errors. Network engineers no longer have to write tedious commands on the CLI (command line interface), with such scripts network engineers can gain more and avoid fewer errors.
Change Management and Version Control
let’s write a script that demonstrates change management and version control
Define Terraform Configuration

Define Backend Configuration for Remote State Management
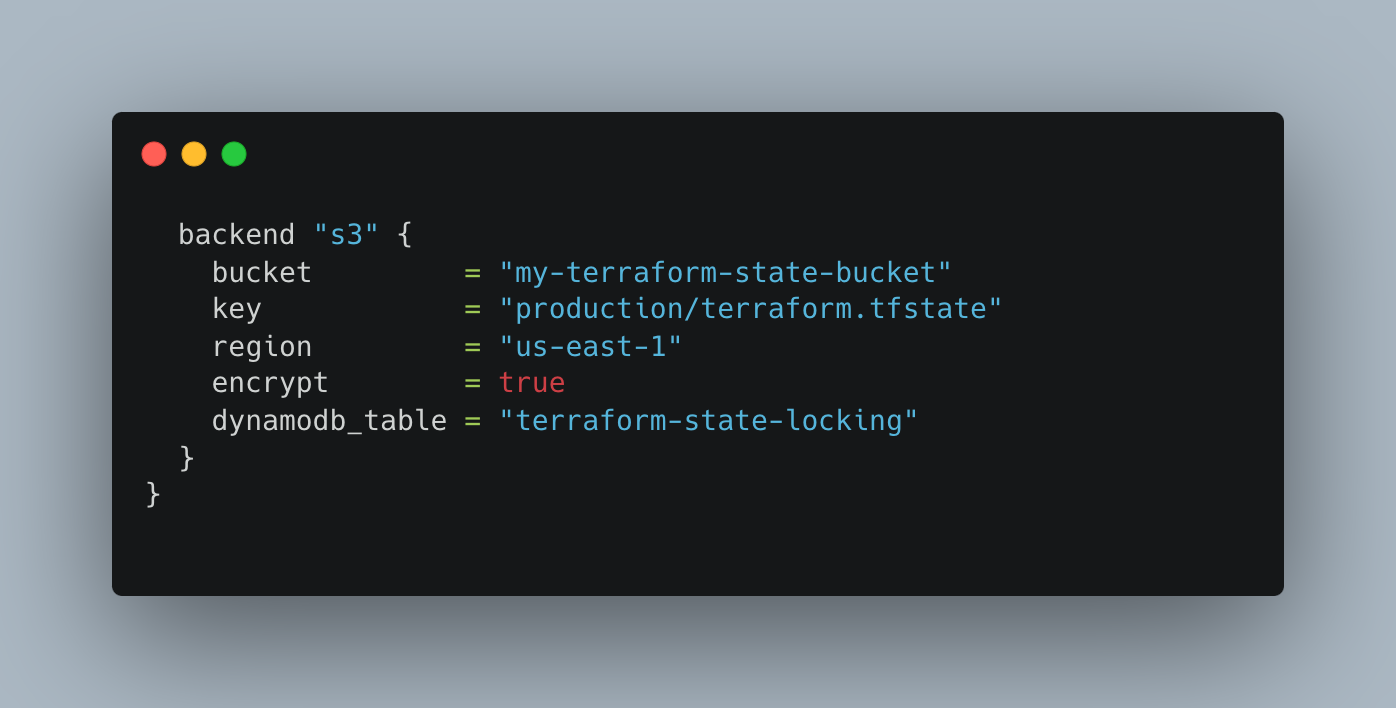
Provider Configuration
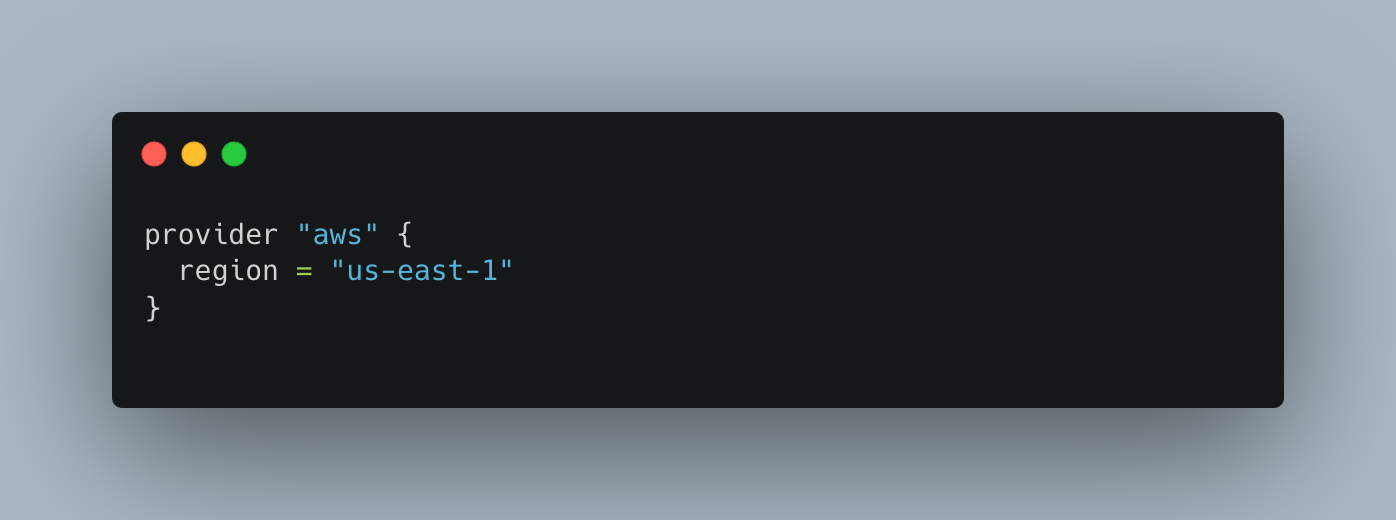
The use of Terraform for automation enhances change management and version control practices, enabling teams to deploy and manage infrastructure reliably, efficiently, and at scale, with scripting anything is possible!
Conclusion
Automation is not a replacement for the network engineering workforce, Instead, it is a chance to provide high-quality services quickly and with less manual labor. The command-line interface (CLI) is no longer sufficient to keep up with the various changes we have in the industry. Network engineers can use automation and tools such as Terraform to enhance many processes, freeing up more time to concentrate on other tasks. The key to success is adaptability!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments