Securely Managing, Distributing, and Scaling Secrets Across Multiple Kubernetes Clusters
Fetch secrets from external secret management systems and securely distribute their content to a multitude of Kubernetes clusters.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeA secret is any piece of information that you want to keep confidential, such as API keys, passwords, certificates, and SSH keys. Secret Manager systems store your secrets in a secure, encrypted format, and provide you with a simple, secure way to access them.
Here are some of the benefits of using Secret Manager:
- Security: Secret Manager uses strong encryption to protect your secrets. Your secrets are never stored in plaintext, and they are only accessible to authorized users.
- Convenience: Secret Manager makes it easy to manage your secrets. You can store, access, and rotate your secrets from anywhere.
- Auditability: Secret Manager provides detailed audit logs that track who accessed your secrets and when. This helps you to track down security incidents and to comply with security regulations.
External Secrets Operator
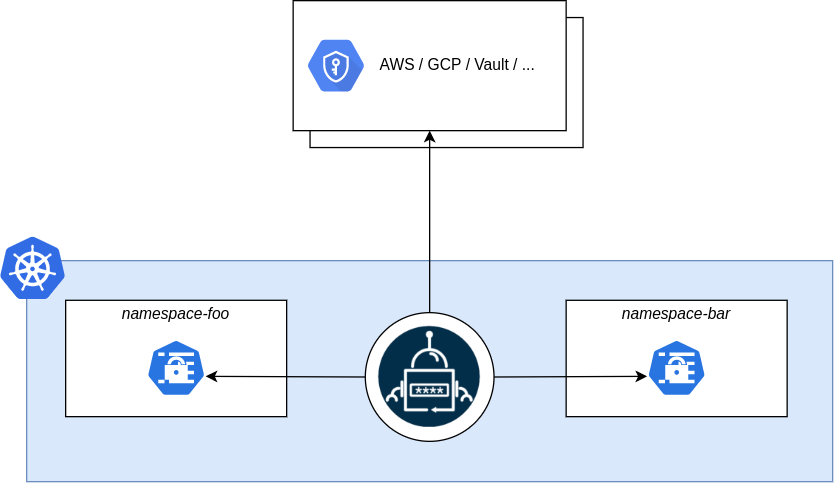
External Secrets Operator is an open-source Kubernetes operator that integrates external secret management systems like AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, Google Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, IBM Cloud Secrets Manager, and many more. The goal of the External Secrets Operator is to synchronize secrets from external APIs into Kubernetes. The operator reads information from external APIs and automatically injects the values into a Kubernetes Secret. If the secret from the external API changes, the controller will reconcile the state in the cluster and update the secrets accordingly.
External Secrets Operator
Distribute Secrets to a Multitude of Managed Clusters
To manage secrets across multiple Kubernetes clusters, you can deploy External Secret Operator in the management cluster and use Sveltos to distribute the secrets to managed clusters.
The integration of External Secret Operator and Sveltos provides a powerful solution for secret management. External Secret Operator fetches secrets from external APIs and creates Kubernetes secrets, while Sveltos efficiently distributes these fetched secrets to the managed clusters. In case of any changes to the secrets in the external API, External Secret Operator updates the secrets in the management cluster, and Sveltos ensures the reconciliation of state in each managed cluster where the secret was distributed.
This combined approach allows for the seamless handling of secrets in Kubernetes, fetching them securely from external systems, and distributing them effectively across a multitude of clusters, bolstering the overall security and management of the Kubernetes environment.
The combined implementation of External Secrets Operator and Sveltos streamlines secret management in Kubernetes, ensuring secure retrieval from external systems and efficient distribution across multiple clusters. This integration offers the following benefits:
- Centralized Management: Secrets are managed and retrieved from external systems within the management cluster, simplifying the process and reducing complexities.
- Enhanced Security: Secrets are encrypted and stored securely in external secret management systems, guaranteeing data confidentiality.
- Automated Updates: As secrets change in the external secret management systems, the External Secrets Operator automatically updates the corresponding Kubernetes Secrets in the management cluster, ensuring synchronization.
- Consistency Across Clusters: Sveltos maintains uniformity by consistently distributing fetched secrets to all managed clusters, creating a unified and secure approach to secret management.
- Scalability: The solution is designed for efficient scaling, accommodating numerous Kubernetes clusters while upholding performance and security standards.
Support This Project
If you enjoyed this article, please check out the GitHub repo for the project (linked earlier). You can also star the project if you found it helpful.
The GitHub repo is a great resource for getting started with the project. It contains the code, documentation, and examples. You can also find the latest news and updates on the project on the GitHub repo.
Thank you for reading!
Published at DZone with permission of Gianluca Mardente. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments