The Integration Maturity Model: Where Does Your Enterprise Fall?
Digital leaders must assess their integration approach, identify their enterprise’s integration capabilities, and move their integration strategy towards collaboration.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freetoday’s digital enterprise leaders must reshape their integration strategy to meet the demands of transformation in an increasingly digital world. for example, cios, it leaders, and enterprise architects must unify enterprise apis to enable cloud application portfolio agility. ctos, digital strategists, and product management need to connect digital business apps to the ecosystems of saas apps used by their employees, partners, and customers. further, api product owners must create personalized api experiences and workflows that are unique to their ecosystem of users.
it’s imperative for these digital leaders to assess their integration approach, identify their enterprise’s current integration capabilities, and learn how to improve and move their integration strategy towards self-service and collaborative approaches.
at cloud elements, we’ve developed a five-tier integration maturity model. each tier is defined by the level of maturity, or proficiency, in each of the five key categories:
-
management.
-
pre-packaged endpoints.
-
patterns.
-
technology.
-
users.
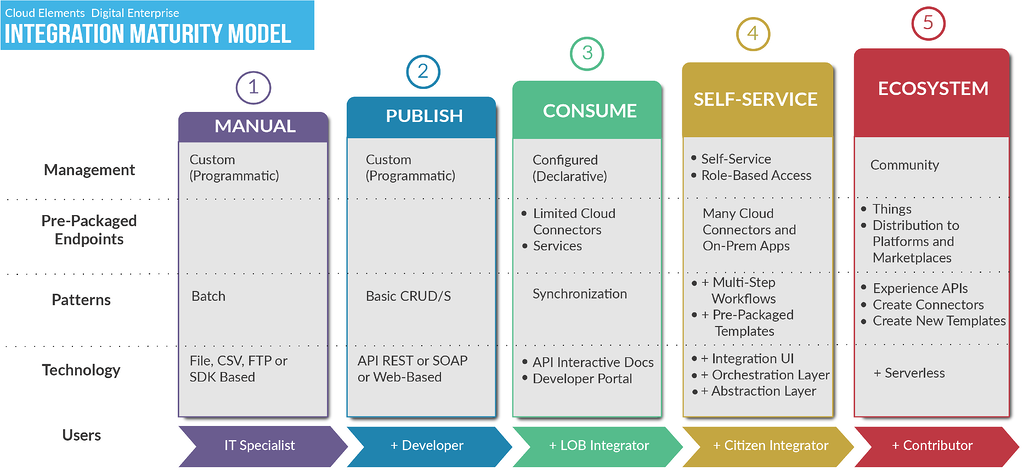
1. manual
this tier has the following characteristics:
- the company has no integration strategy in place and no published apis.
- integration is not recognized as a major need or pain point from the it organization.
- no endpoints or connectors are availabile.
- each integration is manual, custom, typically point-to-point , and done on a one-off basis.
- file (csv or ftp) or sdk-based .
- users: it specialist .
2. published
this tier has the following characteristics:
- the company has an api or apis published .
- the company and/or it department are beginning to recognize integration as a challenge .
- no endpoints or connectors are availabile.
- integration is still point-to-point, custom, and basic crud/s .
- apis are rest, soap, or web-based .
- users: it specialist and developer .
3. consume
this tier has the following characteristics:
- the api is configured and declarative .
- the organization may offer external, third-party integrations, but there is no integration service embedded into their product.
- the organization is competent in integrations offerings .
- a few limited cloud connectors and services are offered.
- synchronization of apis.
- api documentation and a developer portal may be available.
- users: it specialist, developer, and lob integrator .
4. self-service
this tier has the following characteristics:
- embedded integrations offered as self-service or role-based access.
- an api integration strategy has been implemented, exposing apis .
- many cloud connectors and on-premise apps are available.
- there is a single integration strategy group that is responsible for putting multi-step workflows (such as formulas ) in place and creating pre-packaged templates.
- sophisticated integration user interface, orchestration layer, and abstraction layer exist.
- users: it specialist, developer, lob integrator, and citizen integrator .
5. ecosystem
this tier has the following characteristics:
- an integration cloud is in the product offering.
- many pre-packaged connections are offered along with the ability to integrate to things and distribute endpoints into leading platforms and marketplaces (such as aws).
- capable of experience apis, creating new connections , and workflow templates .
- a serverless architecture , or the ability to run code without configuring and managing servers, is supported.
- users: it specialist, developer, lob integrator, citizen integrator, and contributors .
Published at DZone with permission of Ross Garrett, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments