What Are API Gateways?
In this article, see five important use cases for API Gateways.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAn API Gateway is an interface that sits between the application and microservices. Developers use them to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs.
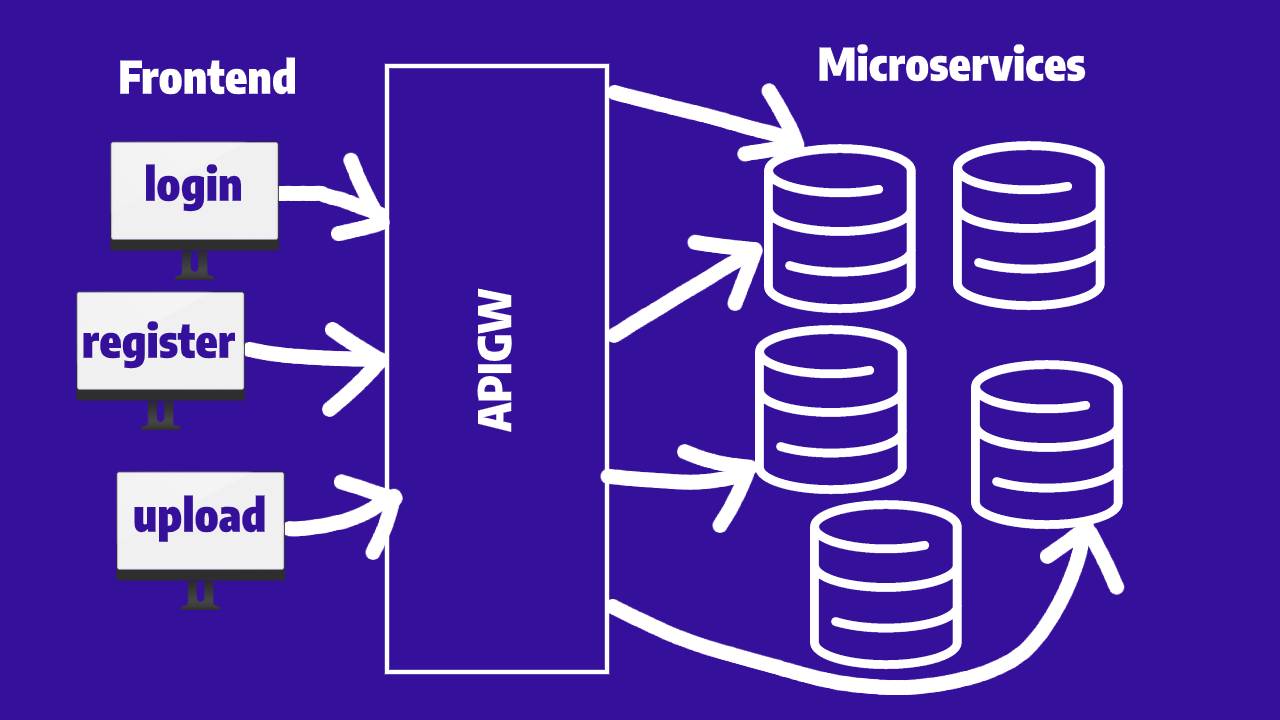
Without using an API Gateway, you’d have to connect all your API resources directly with your user-facing applications, which would make it more difficult to manage responses, implement updates to your business logic, or even secure your API.
Not only will the API Gateway simplify the way you build and manage APIs, but it will boost your security since you are not exposing any endpoints, minimizing the attack vector considerably.
You might also like: API Gateway to the Rescue
What Does an API Gateway Do?
An API gateway can handle any type of interaction between your website, web or mobile application, or even IoT devices and your microservices. Here are some of the most-used scenarios:
Authentication
Your API gateway will integrate with any third-party authentication providers and provide an authentication layer for your application. Here are some of the most common use cases.
User Management
Once the user is registered and authenticated, it will manage the user’s interactions with the website and limit its access based on predefined criteria. The API Gateway will take the pressure of deciding what type of information the user can interact with from your API.
Logging and Monitoring
Since your API Gateway sits between the client and the backend API, it is in a position to track all the interactions between the two, tracking the activities and monitoring all the resources available as well as the response time.
Payload Management
The API Gateway will take the request and route it to the correct microservice and in exchange, receive a response. There are scenarios when that response is not something that the front end can handle and will have to route it to a second microservice or and external service provider before it can return the correct response or format. All of this is done without exposing any of the complex logic or the API endpoints to the client.
Scaling
Last but not least, the need for scaling is a particularity that the API Gateway is in a unique position to calculate based on the frontend and backend activities. Not all of the API Gateways can be expected to provide autoscaling, but they should be able to trigger a service that will deal with it.
Sure, there are lots of other use cases for API Gateways, but these are the most important ones in my opinion. If you think I've missed any, please do let me know in the comments section or via twitter @johndemian.
Further Reading
The Role of API Gateways in API Security
The Two Most Important Challenges With an API Gateway When Adopting Kubernetes
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments